Lately it has change into clear, each within the UK and globally, that interventions are urgently wanted to guard our treasured marine wildlife and safeguard the assets offered to us by the ocean. Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are instruments utilized by marine managers to preserve areas of probably the most weak or ‘invaluable’ species and habitats. Human actions (similar to fishing and useful resource extraction) are restricted or prohibited inside MPAs, permitting habitats and animal communities to get better, and boosting populations past MPA boundaries. So essential are MPAs to world marine conservation efforts, that greater than 100 nations have dedicated to the ‘30 by 30’ Initiative, which advocates the safety of 30% of worldwide ocean by 2030. This ambition was initially led by the UK and is now enshrined as a part of the Conference on Organic Range World Biodiversity Framework targets.
In UK waters our in depth MPA community has expanded over the past decade to incorporate 377 MPAs, with a protection of 38% of our waters. Surpassing the 30% designation goal is an enormously constructive achievement. It’s, nevertheless, simply the beginning of the UK MPA journey. MPAs are unlikely to succeed until they’re fastidiously managed, and their efficiency evaluated. Monitoring (the place data is usually collected by way of time) is a essential a part of this analysis course of to assist scientists perceive whether or not administration is resulting in constructive environmental outcomes. That is partially as a result of MPAs are comparatively ‘younger,’ for instance when in comparison with terrestrial MPAs the place finest monitoring practices and tips are extra properly established. Additionally, the prices and challenges related to monitoring MPAs which might cowl huge areas and quite a lot of totally different species, options and habitats can be larger.
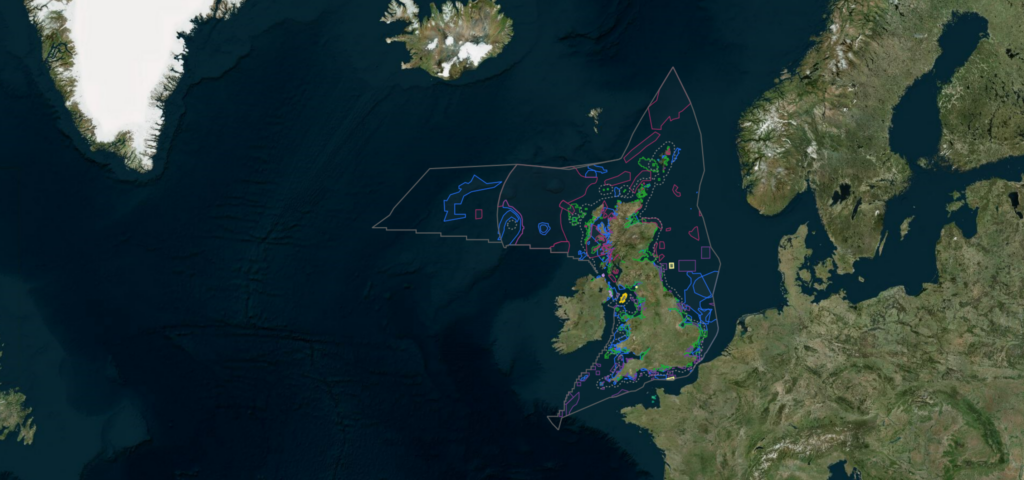
To attempt to deal with this in English waters, Cefas has labored intently with our Authorities companions Pure England and the Joint Nature Conservation Committee (JNCC) for nearly a decade to gather and analyse preliminary, or ‘baseline’ monitoring knowledge at over 60 MPAs. This baselining section, the place the primary set of monitoring knowledge is collected for future comparisons, has proved to be a wealthy studying expertise, offering a take a look at mattress to experiment with totally different monitoring approaches, encounter quite a few challenges, be taught classes and apply options to enhance future monitoring practices.
Some of the essential findings was that whereas nationwide or community scale monitoring approaches are helpful and wanted there’s additionally a have to deal with every MPA as a person entity when it comes to survey planning, knowledge assortment and evaluation, making use of options and refining classes on the MPA degree. An excellent instance of this idea in motion is the Wight Barfleur Reef MPA. Wight Barfleur Reef is a rugged space of bedrock and stony reef within the English Channel. supporting various arrays of sponges, tube worms, anemones and sea squirts. Situated 50 miles from the Dorset coast, protecting 138 kilometres squared and reaching depths of between 25-100m, its advanced geology posed critical challenges for Cefas scientists when figuring out how finest to watch it.

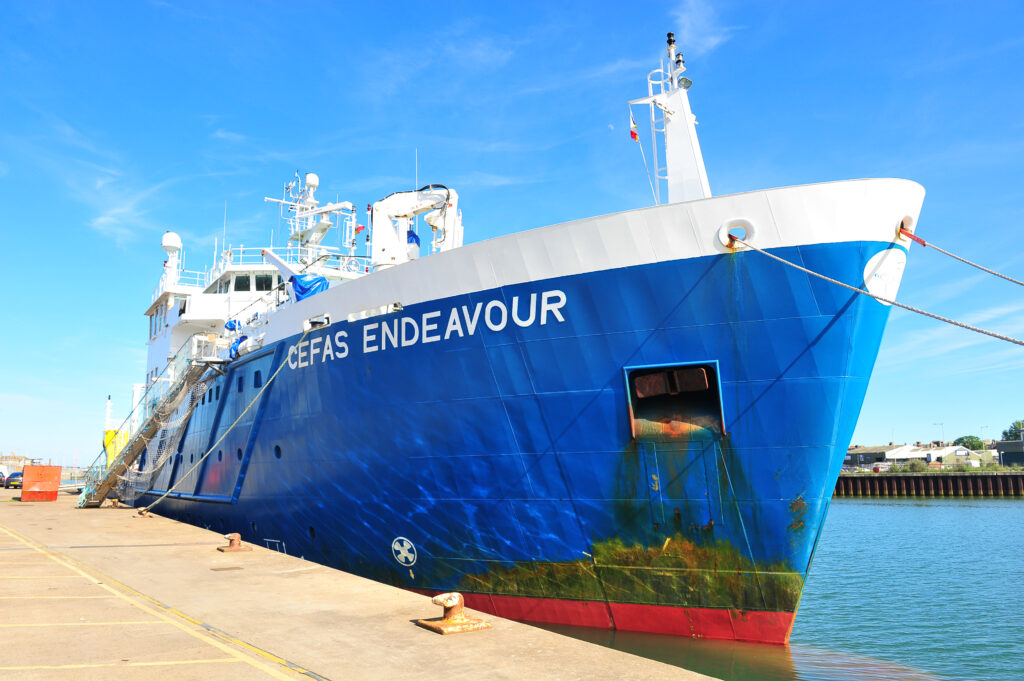
Fastidiously contemplating the distinctive traits of the reef, our scientists used multibeam echosounder bathymetry, digital camera elevation and imagery knowledge to develop an MPA-specific monitoring design and digital camera deployment protocols (see the preliminary monitoring report right here). Subsequent month, aboard the RV Cefas Endeavour, our intrepid survey scientists will revisit the positioning to check this new method . If profitable, it should present a brand new method to gathering knowledge on reef situation and due to this fact enhance the standard of monitoring knowledge from Wight Barfleur Reef. It should even be a brand new milestone within the transferring past ‘baselining’ to gather a second set of information within the time collection that might be used to check the effectiveness of the MPA over time.

One other key affect of the Marine Coverage paper is an settlement between the 4 Authorities our bodies on the place to focus analysis and improvement efforts sooner or later to ship the very best proof for MPA success. Present and future priorities recognized within the report embody: growing metrics to point MPA situation(e.g. Downie et al. 2021), and using novel applied sciences similar to improved imaging programs, environmental DNA evaluation and Synthetic Intelligence for enhancing knowledge high quality and affordability.
There’s nonetheless a lot to do to enhance our understanding and monitoring of weak habitats and species in MPAs. Nonetheless, reflecting on our journey to date has set our route. Going ahead, our MPA monitoring work will embody working extra intently throughout totally different organisations and disciplines inside Cefas. We’re additionally eager to companion with different varieties of survey (e.g. Extremely Protected Marine Areas, Marine Pure Capital, and fish inventory surveys) on the RV Cefas Endeavour to enhance our understanding of wider ecosystem dynamics and challenges, in addition to realising price advantages and efficiencies. Amassing the best doable high quality knowledge might be very important to make sure MPA administration is match for function. This might be essential not simply to hit the 30 by30 goal, however to make sure our MPAs are thriving within the years to come back.


