Two wars raging and geopolitical tensions escalating globally didn’t cease companies from adopting improvements and bettering strengthen their provide chains this 12 months.
Generative synthetic intelligence (AI) burst onto the scene as ChatGPT turned the world’s hottest AI platform, attracting 100 million customers simply two months after its launch. However as companies embrace the know-how to extend productiveness and reduce prices, there at the moment are widespread calls to guard and assist staff, to be sure that automation improves the office and doesn’t find yourself threatening jobs. These efforts are more likely to proceed.
Electrical automobile (EV) adoption is rising shortly in rising economies like India, Thailand and Indonesia, the place low-cost fashions are driving demand.
Stricter rules have prompted corporates to maintain observe not simply of their direct emissions, but additionally these from their suppliers and end-users.
Eco-Enterprise identifies 5 main developments that can form enterprise and society in 2024.
1. Heightened name to guard staff amid newest wave of AI improvements
Quickly advancing know-how has not pushed conversations as considerably as generative AI has up to now 12 months.
By exhibiting the way it can write a science fiction novel in just a few hours to with the ability to work together with purchasers in numerous languages, ChatGPT has stirred controversy because it threatens to displace as many as 300 million jobs through automating them.

Artists and illustrators within the US are utilizing the hashtag #artbyhumans as a type of silent protest in opposition to the surge of AI-generated pictures. Picture: No to AI Generated Photographs
A survey in September by London-based market analysis agency Mintel Developments studied international client behaviour and located that half of the respondents in Asia Pacific fear that AI will make their jobs out of date, regardless of 57 per cent saying they know little about AI.
In the identical evaluation, 69 per cent of respondents mentioned they had been opposed to purchasing from firms who behave unethically by deceptive shoppers and mistreating staff, whereas 73 per cent mentioned firms ought to do extra to deal with inequality like honest pay and assist for susceptible populations.
These findings sign a “sturdy ethical thread” throughout the area that signifies that defending the rights of staff in opposition to inequality and mistreatment will growing turn into the norm, mentioned Matthew Crabbe, Asia Pacific director of Mintel. This consists of wanting into how jobs may doubtlessly be threatened by fashionable know-how,
“A brand new ‘human-as-premium’ label will emerge, giving higher affect to artisans who can tackle the inventive spirit that exists exterior of an algorithm,” mentioned Crabbe.
“As extra companies embrace AI to extend productiveness and reduce prices, there shall be widespread calls to guard and assist staff, reasonably than make them redundant.”
Shoppers will want time to regulate and discover ways to make know-how extra relevant on the particular person degree, sparking new discussions and improvements round find out how to be intentional about mixing the digital and the bodily, Crabbe added.
2. EV quick monitoring in creating Asia
Gross sales of EVs in China have soared in recent times, representing round 1 / 4 of the world’s market. Within the homefront, China’s Hainan province has set Asia’s most formidable goal to part out gross sales of conventional autos by 2030.
Nevertheless, in contrast to photo voltaic know-how, which with its low-cost worth makes it a beautiful funding, EVs haven’t made as a lot impression to the remainder of the creating world on account of comparatively excessive buy costs and a scarcity of obtainable charging infrastructure.
At COP28, 56 rich governments, together with the UK, Sweden and Germany pledged worldwide help spanning finance, provide chain improvement and technical experience for rising markets with the ambition of creating EVs the “most inexpensive, accessible, and engaging possibility in all areas by 2030”.
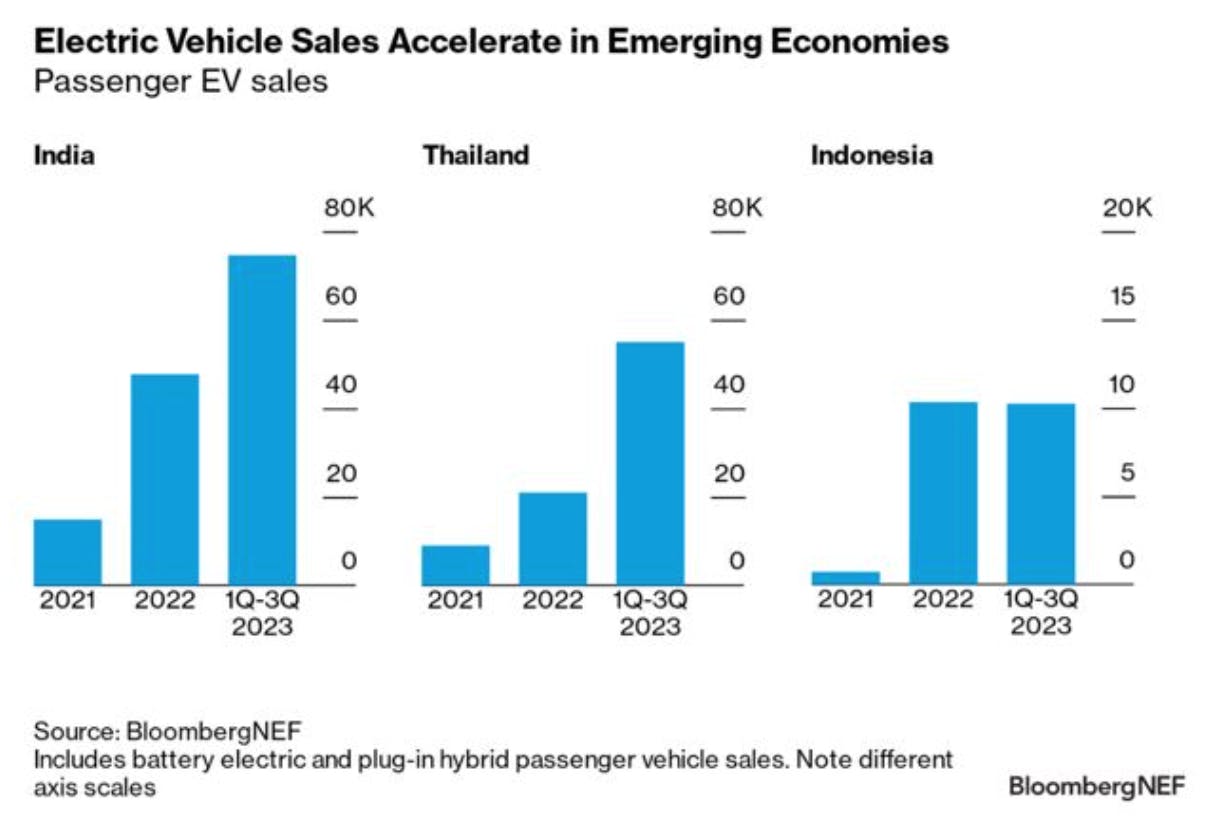
However even with out this international help, international locations in creating Asia like Thailand, Indonesia and India are decided to construct their very own EV industries as alternate options to China.
EVs are already 9 per cent of vehicles bought in Thailand, boosted by a US$1.44 billion plant constructed by Chinese language EV large BYD within the province of Rayong, which can turn into operational in 2024.
Thailand, Southeast Asia’s largest automobile producer and exporter, has supplied incentives together with tax breaks and subsidies to draw EV makers and stimulate demand.
Indonesia, which holds the world’s largest nickel reserves that’s very important for the manufacturing of EV batteries, has been decided to leverage these sources to construct a home EV provide chain. It has aggressively courted international automobile and battery makers via relaxed funding guidelines.
India now has tens of millions of EV house owners, with in style motorbikes, scooters and rickshaws representing greater than 90 per cent of the autos.
The market’s development is due partially to a US$1.3 billion authorities scheme to encourage EV manufacturing within the nation and supply reductions for patrons.
3. Scope 3 disclosure within the highlight
[Click to enlarge] The proportion of world emissions lined by firms with a goal together with Scope 3 emissions reductions has greater than doubled since 2019, however solely represents a 3rd of all firms reporting a goal. Supply: CDP Company Environmental Motion Tracker 2023
There shall be extra expectations from firms to give attention to disclosing not simply direct emissions from their worth chain, but additionally their Scope 3 or oblique emissions from suppliers and end-users, mentioned Ivan Li, director of technique and implementation, Asia Pacific for power consultancy ENGIE Influence.
Li cited a 2023 report of the CDP’s Company Environmental Motion Tracker which revealed how the proportion of world emissions lined by firms with a goal together with Scope 3 has greater than doubled since 2019,
“It’s an indication that firms are waking as much as the significance of tackling oblique emissions and actively taking steps to cut back their total environmental impression,” he mentioned. “Companies are additionally gaining a clearer understanding of how addressing Scope 3 emissions is essential of their journey in direction of attaining web zero. We count on firms to face elevated scrutiny and stress to step up and supply extra complete reporting in 2024.”
A big a part of this elevated consideration could be attributed to new laws imposing stricter environmental reporting tips and sustainability practices, he added.
In June, the Worldwide Sustainability Requirements Board (ISSB) revealed its disclosure requirements, which cowl normal sustainability considerations (IFRS S1) and local weather disclosures (IFRS S2).
The heightened scrutiny from authorities our bodies and key stakeholders are prompting corporates to take proactive measures to reinforce transparency. Many are choosing voluntary reporting buildings, demonstrating their dedication via avenues like pursuing the approval of science-based targets by the Science Primarily based Targets initiative (SBTi), which mandates reporting on related Scope 3 emissions.
4. Steerage away from greenwashing

Starbucks Korea has been recognised by the federal government for its low-impact recycling of its espresso grounds. Picture: Mintel
Belief and reassurance will add a brand new layer to environmental, social, and company governance (ESG) initiatives as companies undertake local weather adaptability of their enterprise practices, mentioned Mintel’s Crabbe.
Mintel discovered that 74 per cent of these surveyed in Asia Pacific count on manufacturers to take the lead on addressing environmental points and spearhead local weather options as a substitute of counting on decades-long plans on carbon discount made by governments and establishments.
“Shoppers sense that many firms will not be being clear about what they’re doing to have a constructive local weather impression, and the constructive impact their actions is having. Individuals wish to be extra sustainable however lack info on how to try this. Manufacturers could make this simpler by being extra clear,” mentioned Crabbe.
They’ll do that by explaining how they cut back meals waste, power and water use, packaging waste of their merchandise, and the way they’re working in direction of adopting a round economic system enterprise mannequin, or how they’re placing a certain quantity of their earnings again into sustainability efforts or supporting moral organisations, he added.
5. Will election fever in Asia impression the sustainability agenda?
For the primary time ever, there shall be 40 nationwide elections all around the world within the coming 12 months, 1 / 4 of which shall be in Asia.
However observers have mentioned that incoming administrations are more likely to proceed the insurance policies of and maintain related stances on local weather change as their predecessors.
Indonesia’s wildly in style chief Joko Widodo had prided himself on his transfer to ban nickel ore exports three years in the past as a profitable option to develop the native smelting business and supply higher welfare for the nation. He expects his successor to proceed the programme.
However Rere Christanto, supervisor of mining and power marketing campaign of Indonesian Discussion board for the Surroundings (WALHI), mentioned that neither Widodo nor any of the presidential candidates speaks in regards to the impacts of the downstream nickel business in Indonesia, resembling lack of forest areas, excessive crime charges and the violation of native environmental legal guidelines by companies within the nickel sector.
“I feel it’s harmful that not one of the presidential candidates have spoken overtly in opposition to environmental destruction and threats to communities from the nickel business,” mentioned Rere.
“Events supporting the candidates additionally beforehand had a observe report as proponents of mineral and coal legal guidelines that are the idea for accelerating injury attributable to mining in Indonesia.”
The identical is the case in India the place frontrunner prime minister Narendra Modi has promised 500 gigawatts of unpolluted power earlier than 2030, however has mentioned little about reforms for coal. Elections are unlikely to vary that, say observers.
Are there different rising developments that we now have missed? Tell us by writing to information@eco-business.com. This story is a part of our 12 months in Evaluation collection.


