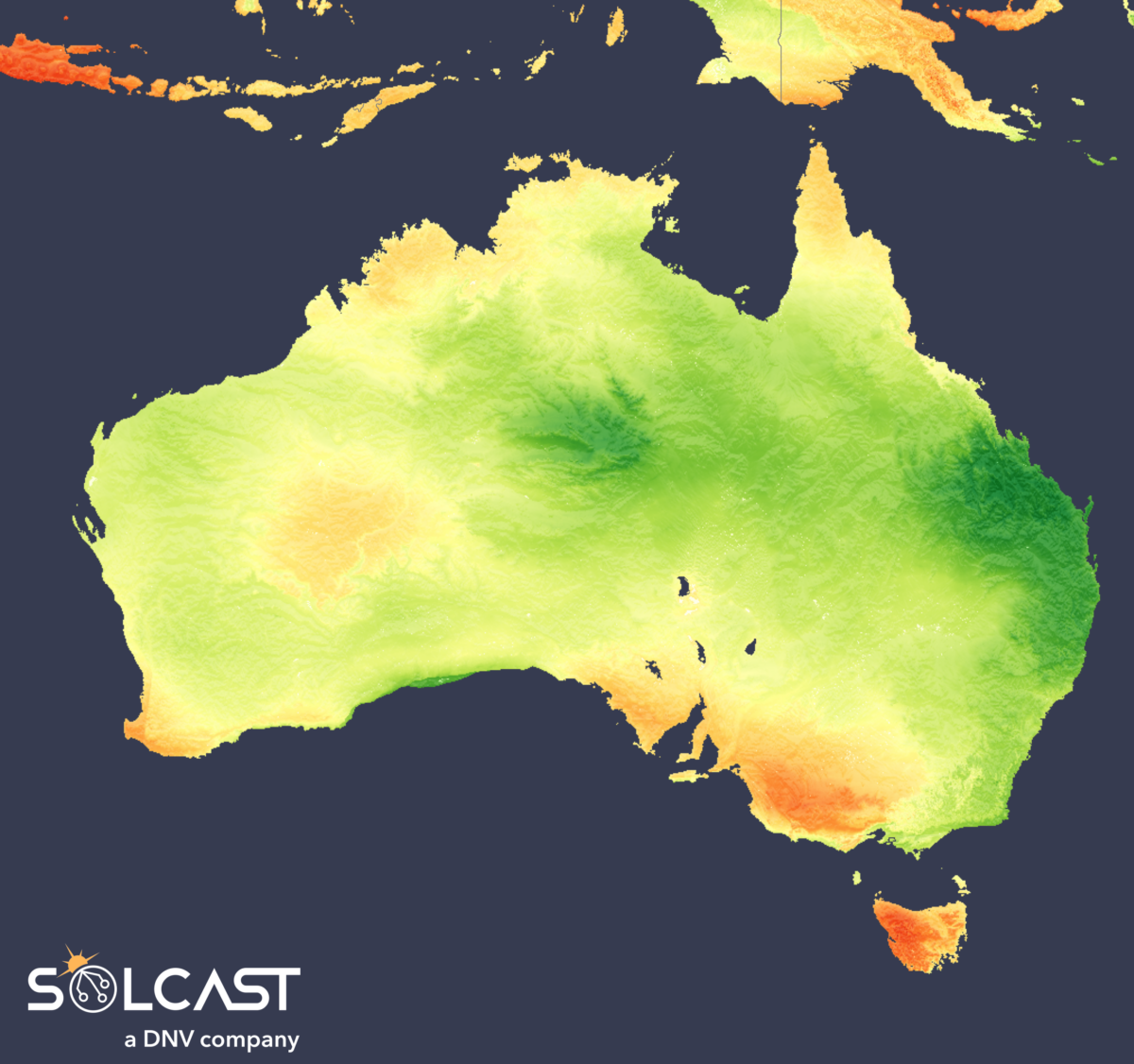
In a brand new weekly replace for pv journal, Solcast, a DNV firm, stories that jap Australia’s behind-the-meter normalized technology has fallen by 10% to fifteen% yr on yr.
Regardless of the growing El Nino, jap Australia’s behind-the-meter normalized technology is down 10% to fifteen% in comparison with final yr. This growth is a end result as a result of a moist and cloudy finish to spring, which countered the standard drier, sunny circumstances related to El Nino.
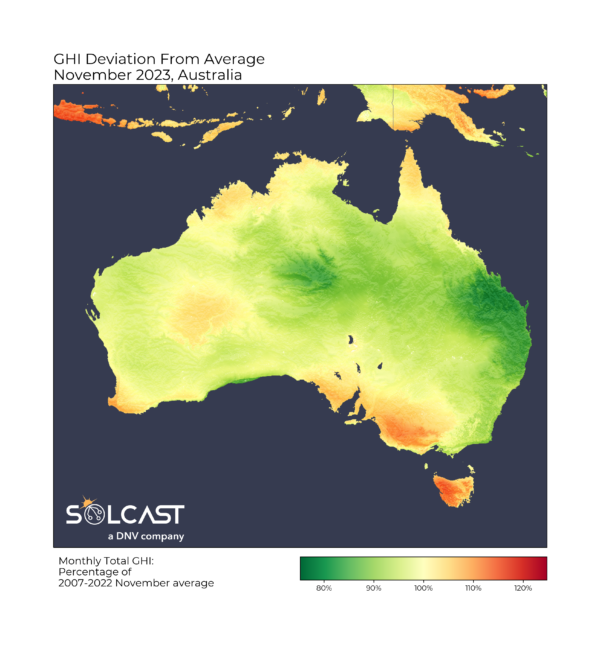
Utilizing the Solcast API to mannequin behind-the-meter technology at hundreds of factors, latest knowledge evaluation exhibits how November 2023 rooftop photo voltaic carried out throughout the nation, in comparison with 2022.
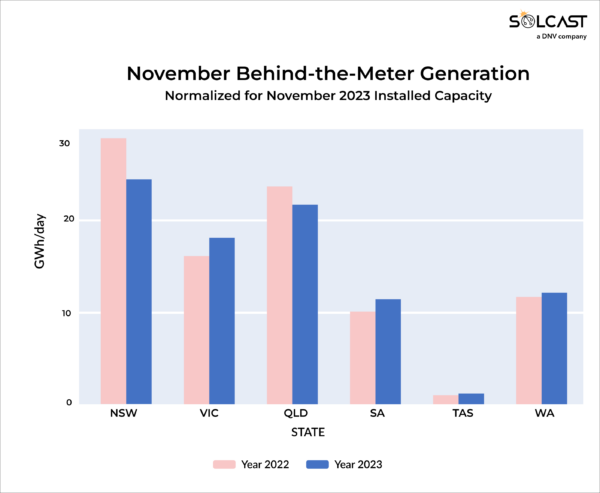
Most photo voltaic property on Australia’s east coast underperformed as a result of cloudier circumstances by November. In New South Wales, behind-the-meter normalized technology fell 15% from 2022. Queensland skilled a smaller lower of about 10%.
These reductions had been largely as a result of persistent excessive stress within the Tasman Sea, which directed north-easterly winds into jap Australia, resulting in a extra moist and unstable air mass. Because of this, November skilled elevated storm exercise and cloudiness, notably affecting coastal areas the place nearly all of residential and commercial-industrial photo voltaic techniques are positioned.
In distinction, Victoria skilled a ten% improve in November’s year-on-year normalized behind-the-meter technology. This was primarily because of the similar high-pressure system within the Tasman Sea suppressing floor chilly fronts that have an effect on the west of the state. Chilly fronts often convey south-westerly winds and a cool, moist air mass from the Southern Ocean to western Victoria.
Nevertheless, their suppression this yr led to sunnier circumstances, notably within the west, which incorporates Melbourne – a excessive residential PV-density inhabitants middle. Regardless of the jap a part of Victoria experiencing about 10% decrease irradiance just like the remainder of the east coast, the sunnier west compensated for this when it comes to behind-the-meter technology.
Regardless of its giant space, behind-the-meter PV in Australia is extremely concentrated as a result of its extremely urbanized and densely populated areas. Australia has the best per-capita PV put in capability on the planet, rising at a fee of greater than 10% yearly. Latest knowledge from SunWiz exhibits that over 330 MW of recent rooftop photo voltaic techniques had been put in in November 2023, the most important month for rooftop photo voltaic installations ever seen in Australia.
Australia’s excessive focus of solar energy presents challenges in managing uncertainty in behind-the-meter technology and underlying demand. In a number of states, daytime peaks of rooftop photo voltaic technology are pushing demand under base load technology from coal. Correct photo voltaic knowledge and forecasting, like has been used on this evaluation, are vital in addressing these challenges, guaranteeing environment friendly grid operation and maximizing the advantages of photo voltaic vitality.
Solcast produces these figures by monitoring clouds and aerosols at 1-2km decision globally, utilizing satellite tv for pc knowledge and proprietary AI/ML algorithms. This knowledge is used to drive irradiance fashions, enabling Solcast to calculate irradiance at excessive decision, with typical bias of lower than 2%, and in addition cloud-tracking forecasts. This info is utilized by greater than 300 corporations managing over 150 GW of photo voltaic property all through the world.
The views and opinions expressed on this article are the creator’s personal, and don’t essentially mirror these held by pv journal.
This content material is protected by copyright and will not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and want to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.