A analysis group in Switzerland has enhanced the hail check stand to measure the influence of ice balls with bigger diameters and better velocity on photo voltaic panels. The brand new testing strategy will reportedly allow photo voltaic panel makers to evaluate their merchandise with ample security margins.
Scientists on the College of Utilized Sciences and Arts of Southern Switzerland have developed a novel hail check for photovoltaic panels that considers the influence of enormous, high-velocity ice balls.
The analysis crew pressured that conventional hail assessments performed by the IEC 61215-2 customary often assess the influence of ice balls with a 25 mm diameter and 80 km/h velocity. It additionally stated, nonetheless, that the Swiss Affiliation of Cantonal Hearth Insurers – the Vereinigung Kantonaler Feuerversicherungen (VFK) – established a minimal requirement of 30/40 mm and added that Switzerland’s SUPSI PVLab is presently planning to create a hail check stand to achieve 100 mm in diameter and 166 km/h in velocity.
“The rise in ice ball diameter necessitates the analysis of pattern preparation, repeatability, and representativeness, in addition to the power to deal with excessive speeds with excessive lots to cut back uncertainty in influence vitality, as required by the Swiss requirements,” the researchers stated.
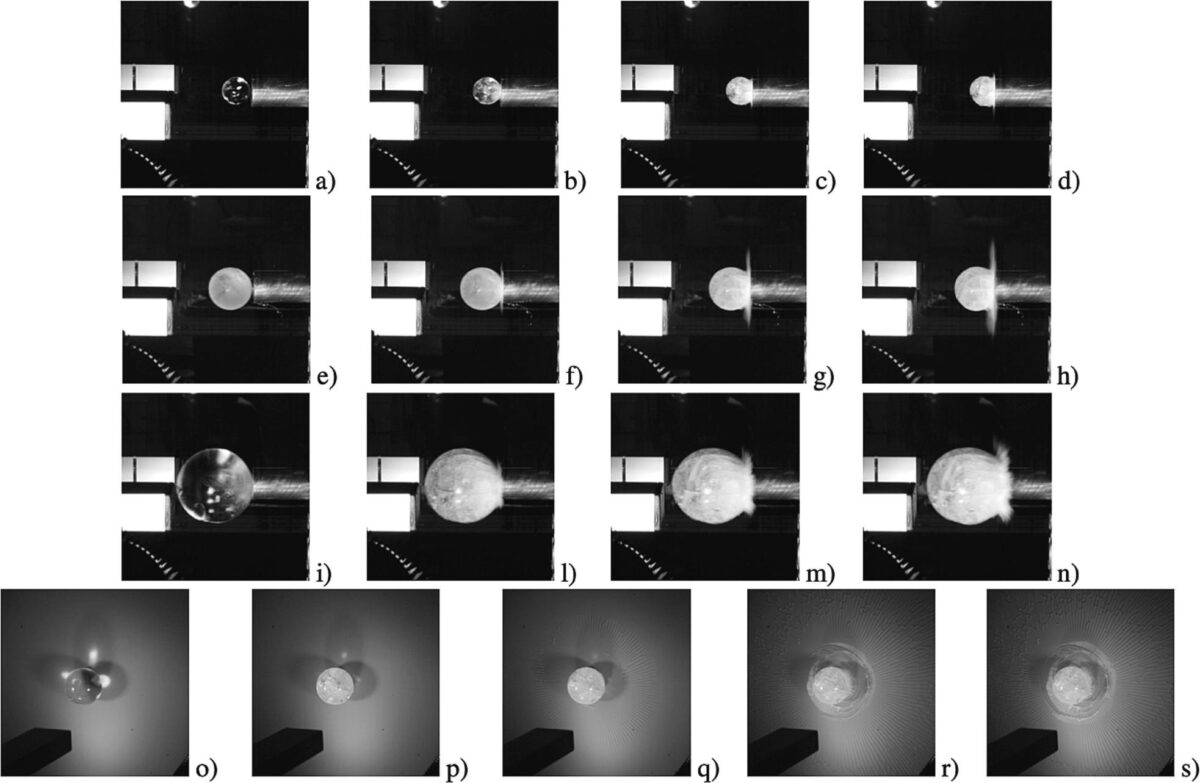
They utilized a Hopkinson bar, and a 30 mm aluminum bar to research the waveform ensuing from the collision of the ice balls. In addition they used a strain-gauge station, a fuel gun for ice ball acceleration, and a digital camera for quick picture recordings.
The fuel gun was designed to shoot ice balls with diameters of 25 mm, 40 mm, and 70 mm onto the Hopkinson bar. “A spherical plexiglass tube with completely different inside diameters was used to information the spherical ice inside it,” researchers defined. “To measure the rate of the spherical ice specimens, a laser sensor was positioned on the finish of the tube.”
The lecturers shot the three balls on the identical velocity and at two completely different frozen temperatures, −5 C and −20 C, to match loading versus time response.
Analyzing the samples having 40 mm diameters, they ascertained that the temperature lower brought about a double loading fee, which in flip brought about the next stress fee on the bar.
“Within the case of 25, 40, and 70 mm ice balls at −20 C, peak forces are roughly 70%, 59%, and 44% increased than these at −5 C on the identical velocities,” they additional defined. “For 25, 40, and 70 mm, ice reaches its peak drive in a shorter period of time at −20 C, which is 30%, 21% and a couple of% decrease than at −5 C.”
The evaluation confirmed that decrease temperature ends in the next peak drive and a shorter peak time. “Utilizing these preliminary outcomes, the venture will transfer ahead with its future duties, together with the evaluation of hail stone harm utilizing a multispectral digital camera, the evaluation of PV panels of various ages, ice mechanical characterization in the identical pressure fee vary, and FEM modeling of phenomena,” the scientists concluded.
Their findings had been introduced within the research “Superior characterisation of photovoltaics for hail resistance,” printed in Supplies Letters.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and want to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.