Within the run-up to the twenty eighth Convention of the Events (COP 28) on local weather change, Southeast Asia is within the highlight not solely as a hotspot for local weather impacts but additionally for the urgency to take local weather motion. Policymakers within the area see the crucial for local weather mitigation and adaptation however underscore the inadequacy of local weather finance as an obstacle. The area, in line with one estimate by the Asian Improvement Financial institution, requires US$210 billion yearly via 2030 for local weather infrastructure funding. That will be 12 per cent of the US$1.8 trillion of sustainable infrastructure funding wanted yearly via 2030 for rising economies (excluding China), as estimated by an unbiased panel for the 2023 G-20 conferences.
A major proportion of the funding wanted stems from the price of transitioning away from carbon-intensive industries, investing in renewable vitality, and bettering vitality effectivity. Moreover, defending forests and adopting sustainable land use practices are very important for carbon sequestration. Adaptation measures are additionally wanted, together with strengthening transportation and vitality infrastructure to face up to excessive climate, discovering drought-resistant crop varieties, and activating early warning techniques for pure disasters.
The scale of the wanted local weather funding interprets roughly to 4-5 per cent of the GDP of Southeast Asia and rising economies. An evaluation of the US$1.8 trillion means that two-thirds of the determine, or US$1.2 trillion, must be raised domestically (illustrated in Determine 1). The remaining US$0.6 trillion might come from worldwide sources. About half of the US$0.6 trillion would come from personal debt and fairness flows and the opposite half from public sources, primarily multilateral growth banks (MDB). Contemplating that the World Financial institution Group’s whole lending was US$71 billion and the Asian Improvement Financial institution’s US$20 billion in 2022, the local weather financing hole would look like giant.
Subsequently, there may be an pressing must encourage a number of sources of local weather finance from a number of stakeholders utilizing progressive financing mechanisms. The political constraints to opening new avenues away from the monopolistic or oligopolistic maintain of state-owned enterprises have to be addressed. It could assist to strengthen coverage and regulatory frameworks, together with value alerts, governing local weather finance. These alerts embrace monetary incentives for inexperienced bonds. For instance, government-linked and different state-owned enterprises in Indonesia ought to be capable of subject inexperienced bonds to complement inexperienced infrastructure tasks which might be financed by the federal government finances. MDBscan enhance home inexperienced bond markets in Indonesia and different international locations by offering ensures in opposition to the lack of capital.
Steps to boost the profile and credibility of inexperienced finance in home markets will assist. As funding in renewables and different inexperienced ventures are usually threat inclined, higher transparency within the nature and depth of these dangers will assist. For instance, accounting for local weather impacts in asset valuation will be performed. For example, the Philippines or Vietnam — international locations with excessive publicity to excessive climate — would acquire from extra clear accounting of the dangers. Higher communication also can assist. To advertise a greater understanding of inexperienced bonds and different index-linked merchandise, Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, the Philippines and Vietnam have developed taxonomies that set up a standard language for inexperienced funding.
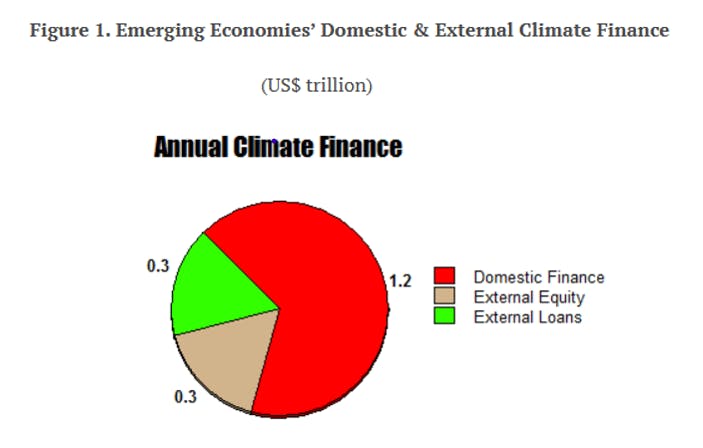
The 2023 G20 conferences recommend that US$1.8 trillion of sustainable infrastructure funding is required yearly as much as 2030 for rising economies, excluding China. Two-thirds, or US$1.2 trillion, must be raised domestically. Picture: Vinod Thomas/ Fulcrum
Carbon markets and buying and selling, underpinned by quantitative restrictions or taxes on carbon, can present one other supply of finance for Southeast Asia. By placing a value on carbon, companies are, in a technique or one other, motivated to cut back emissions. These mechanisms create financial incentives for emission reductions by permitting the shopping for and promoting of carbon credit. Southeast Asian international locations can take part in worldwide carbon markets, producing income from emissions reductions achieved via their local weather tasks.
Given the scale of the financing gaps, Southeast Asia also needs to faucet into grassroots financing mechanisms. Group-based initiatives, crowdfunding, and social impression bonds can empower native communities to contribute to local weather tasks. This bottom-up strategy helps local weather finance to achieve these most susceptible to local weather change. Frank Lysy, a former World Financial institution economist, notes that in instances the place an enormous scale of investments passed off, be it in mobile cell companies or digital applied sciences, the viability of the applied sciences and supportive regulatory frameworks had been key, not top-down financing by the general public sector. Local weather finance is totally different from these situations, given the huge spillover hurt inherent in emissions and the dangers of fresh know-how. Nonetheless, the function of grassroots financing must be capitalised on.
The character and even the extent of local weather finance will also be influenced by giving higher play for nature-based options outlined by the Worldwide Union for Conservation of Nature as “actions to guard, sustainably handle, and restore pure or modified ecosystems”. One instance of such an initiative is the East Asian–Australasian Flyway. The flyway, one of many world’s nice flyways of migratory birds, utilises nature-based options which might be additionally climate-friendly. The Philippines can be making an attempt to make use of nature-friendly options to mitigate flood dangers in six river basins.
In step with the agenda for COP 28, Southeast Asia must mobilise sizable assets to deal with mitigation and adaptation wants. Regardless that local weather change is part of these different issues, policymakers are stretched by different pressing priorities and need to deal with a number of points, equivalent to meals insecurity to well being care. Given such competing priorities, the urgency of local weather motion appears to take a backseat within the eyes of the politicians and the general public. However given the escalating local weather disaster and its sizeable financing necessities, it would take a mixture of avenues — home funding, multilateral assist, carbon markets, personal sector engagement, and grassroots financing — to bridge the hole.
Vinod Thomas is presently Visiting Senior Fellow on the ISEAS – Yusof Ishak Institute, and beforehand Visiting Professor at Nationwide College of Singapore. He’s a Distinguished Fellow in Improvement Administration on the Asian Institute of Administration, Manila, and a member of the advisory panel on local weather change at CSEP, New Delhi.
This text was first revealed in Fulcrum, ISEAS – Yusof Ishak Institute’s blogsite.


