A brand new examine categorizes volcanoes within the Southern Andes area to assist establish websites with the very best potential for high-enthalpy geothermal vitality.
A examine by researchers on the Andes Middle of Excellence in Geothermal Vitality (CEGA) in Chile has proposed a geoscientific mannequin for classifying volcanoes within the Southern Andean Volcanic Zone (SVZ). By this analysis, two volcanic complicated and 5 volcanoes have been recognized as having potential for high-enthalpy geothermal vitality manufacturing.
The paper “Decoding the state of stress and fluid pathways alongside the Andean Southern Volcanic Zone” by Pérez et al has been printed within the journal Communications Earth & Setting.
The South Andean Volcanic Zone
The SVZ runs by way of central to southern Chile and is characterised as having a few of the most energetic volcanoes within the area. Though the SVZ and its volcanoes are properly described within the literature, little is understood about what occurs beneath them: how the magmas movement, what kinds of stress they’re accumulating and what are the underlying tectonic processes that govern their actions.
To characterize these volcanoes, the researchers performed subject expeditions and complemented their efforts with a assessment of earlier research on seismology and structural geology of the SVZ to develop physical-mathematical fashions and simulations to categorize the volcanoes based mostly on conduct patterns.
“One of many largest challenges in volcanology is detecting patterns. Volcanoes are rebellious constructions, every with its personal traces, markers and indicators, which makes them troublesome geological constructions to review. On this context, using classes is complicated, however on the similar time, vital,” mentioned Dr. Nicolás Pérez , researcher at CEGA and lead creator of the examine.
Three classes recognized
Three patterns – Sort A, Sort B, and Sort C – have been recognized by the paper. Of the three, Sort B volcanoes have been cited as those who would have the very best potential for high-enthalpy geothermal exploration. These volcanoes are characterised by having a magmatic chamber at comparatively shallower depths (lower than 10 km) which might favor the circulation of magmatic and hydrothermal fluids within the subsoil.
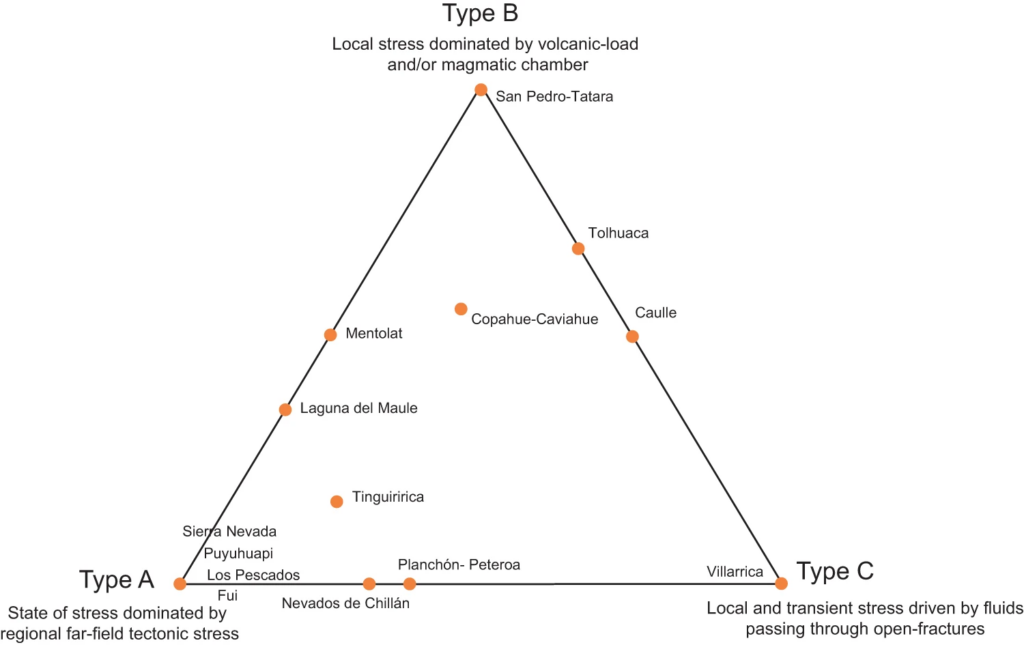
Sort B volcanoes embody the San Pedro-Tatara volcanic complicated, the Puyehue-Cordon Caulle volcanic complicated, and the Copahue, Caviahue, Tinguririca, Tolhuaca, and Mentolat volcanoes.
“The pressures required to generate fractures or channels that enable the circulation of sizzling fluids are the bottom in sort B volcanoes, which makes them good candidates for geothermal manufacturing,” mentioned Dr. Pérez.
On the opposite arms, Sort A volcanoes are produced by stress on the contact between the Nazca and South American plates, whereas Sort C volcanoes might be associated to historical faults indirect to the arc. Sort C volcanoes are additionally essentially the most energetic based mostly on historic information, accounting for greater than 90% of the historic eruptions recorded within the final 300 years have occurred in such a volcano.
A world implication
The analysis paper states that the outcomes introduced are based mostly on the at the moment out there data, however extra sort B volcanoes could also be recognized if extra knowledge is introduced. It additionally notes that the stress patterns recognized within the examine aren’t restricted to the Southern Chile Volcanic Zone. The Sort A sample, as an illustration, has been described in particular volcanic arcs in Japan, Indonesia, and the US.
“There are few research on regional stress regimes in volcanic arcs all over the world. These research are necessary not just for their implications in Chile, but additionally as a result of these fashions might be utilized in different components of the world,” concludes Dr. Pérez.
Supply: Universidad de Chile


