Air high quality in Southeast Asia worsened considerably in 2023, a 12 months when transboundary haze exacerbated by the El Niño climate phenomenon, proliferating coal energy and automobile emissions contributed to rising particulate matter air pollution (PM2.5) in eight out of 9 nations studied by environmental tech agency IQAir.
IQAir tracks PM2.5 information from residents who use its air high quality screens. PM2.5 is particle matter measuring as much as 2.5 micrometres in diameter or smaller that may penetrate deep into the lungs, inflicting well being issues akin to coronary heart illness, bronchial asthma, and low start weight.
Solely three out of 357 Southeast Asian cities met the World Well being Organisation’s (WHO) PM2.5 public well being guideline of not more than 5 micrograms of particulate air pollution per cubic metre (µg/m3) in 2023 – down from eight regional cities in 2022.
The Philippines was the one Southeast Asian nation to document higher air high quality in 2023 than in 2022, with a ten per cent drop in PM2.5 ranges.
Indonesia was by some margin Southeast Asia’s most polluted nation in 2023, a 12 months when common particulate air pollution elevated by 20 per cent.
The sprawling archipelago is house to Southeast Asia’s most polluted metropolis, capital Jakarta, the place air pollution ranges are on common greater than 20 instances above the extent deemed protected to breathe by WHO, in addition to the regional bloc’s cleanest, the mountainous West Sulawesi metropolis of Mamuju, the place pollutions ranges are on a par with some Scandinavian nations.
Seven cities in Indonesia, Vietnam – house to the area’s second most polluted metropolis, Hanoi – and Thailand – which was hit by extreme haze from agricultural burning in its northen areas – exceeded the WHO annual PM2.5 guideline really useful ranges by greater than ten instances in 2023, in comparison with 2022 when no metropolis exceeded an annual common of fifty µg/m3.
Singapore was Southeast Asia’s least polluted nation, albeit with common air pollution ranges of 13.4 µg/m3 – greater than 4 instances above WHO’s protected benchmark.
PM2.5 ranges practically tripled in Cambodia, elevated by 30 per cent in Malaysia, 28 per cent in Thailand, and 9 per cent in Vietnam final 12 months.
El Niño circumstances delaying the onset of the wet season and its mitigating impression on PM2.5 ranges had been cited as among the many important causes for the air pollution spike in Southeast Asia. Main air pollution sources included energy technology, business, street site visitors, and open burning.
Persistent unhealthy air high quality prompted the Affiliation of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) to arrange a particular unit to deal with air air pollution final 12 months. Environmental group Greenpeace referred to as on the area’s governments to introduce home legal guidelines to fight transboundary air air pollution in order that firms linked to cross-border smog are held to account.
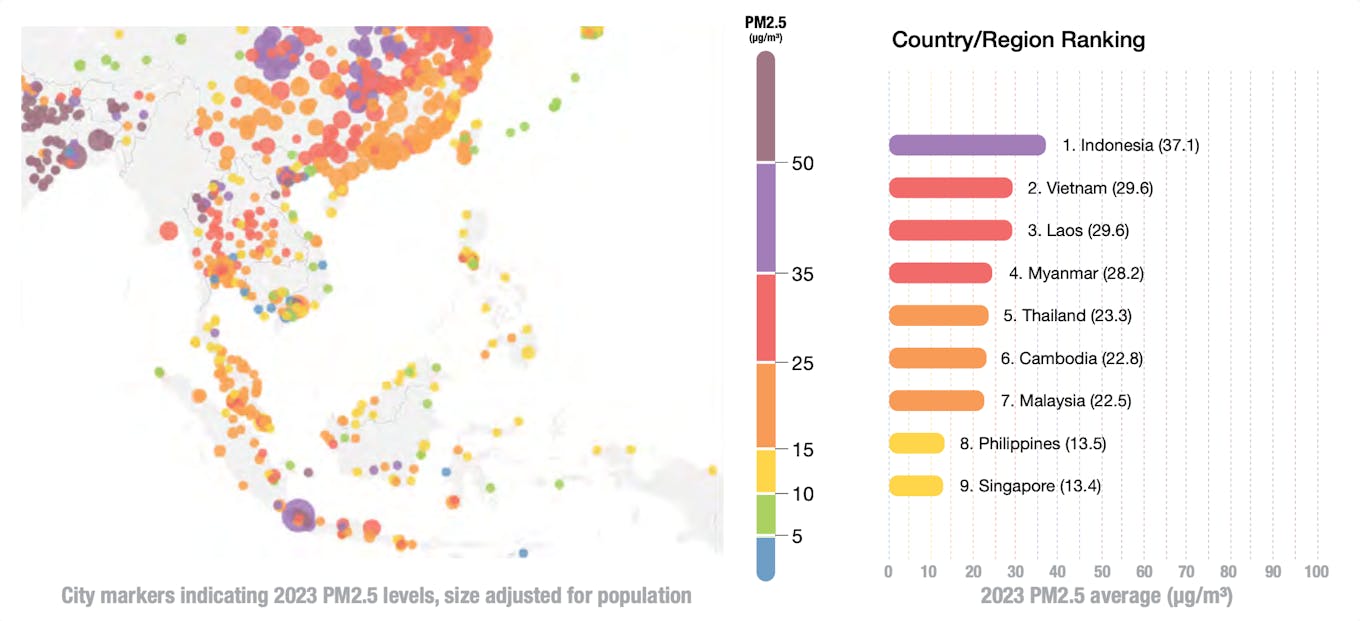
Indonesia had the dirtiest air in Southeast Asia final 12 months, whereas Singapore had the cleanest. Supply: IQAir
China’s spectacular air pollution management track-record ends
China has been championed as a worldwide case research for efficient air pollution management lately, significantly in its capital, Beijing. However the world’s largest greenhouse gasoline emitter’s five-year historic development of declining PM2.5 concentrations led to 2023 with a 6.3 per cent nationwide improve in particulate air pollution.
Thick smog returned to Beijing in 2023, the place residents skilled a 14 per cent improve within the annual common PM2.5 focus.
Some 70 per cent of China’s emissions will be attributed to coal energy, with mud storms, industrial exercise, family strong biomass gasoline burning and transport including to the smog.
China elevated approvals for coal-powered energy vegetation in 2023, with 243 gigawatts of coal-fired capability permitted or below building – a development that jars with the nation’s ambition to realize net-zero emissions by 2060.
Elsewhere in East Asia, Japan, South Korea, Taiwan – which noticed the largest leap in air air pollution in East Asia –Hong Kong and Macau all recorded deteriorating air high quality in 2023.
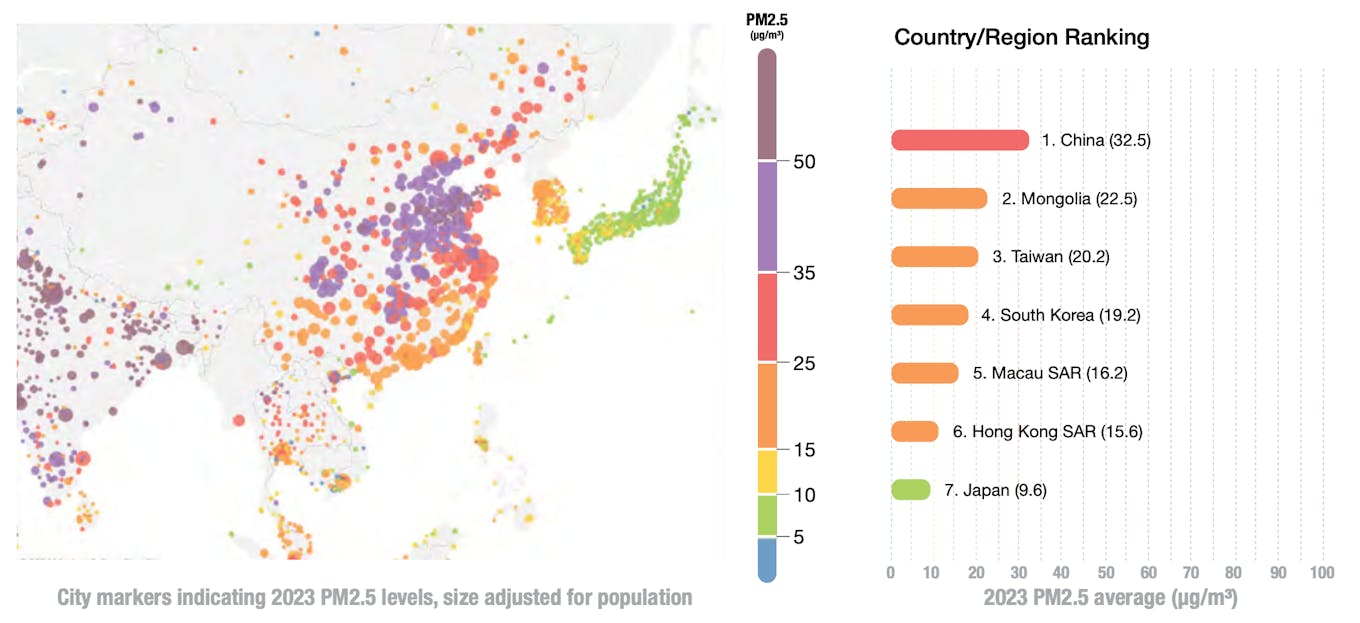
All of East Asia’s high 15 most-polluted cities in 2023 are in China, with Hotan within the arid Tarim Basin area of southwestern Xinjiang, the regional bloc’s most polluted metropolis. Supply: IQAir
World’s most polluted area – South Asia – will get extra polluted
Nearly two-thirds (31 per cent) of South and Central Asia’s cities recorded PM2.5 concentrations of greater than 10 instances WHO’s really useful ranges – a stage that enormously exceeds some other area within the report.
Bangladesh is the area’s – and world’s – most polluted nation total. The nation’s annual common PM2.5 focus rose to 79.9 µg/m3 in 2023, marking the primary improve in air pollution since 2018. Air pollution within the capital, Dhaka, jumped by 20 per cent final 12 months.
Brick manufacturing is cited as a standard type of air air pollution in Bangladesh, with floor mud, factories, family cookstoves, plastic trash incineration, and unlined landfills different main sources.
Air pollution ranges additionally elevated in India, to 54.4 µg/m3, and rose by 10 per cent in New Delhi, the world’s most polluted metropolis, to 92.7 µg/m3 – greater than 18 instances above WHO’s safe-limit.
Fourteen of the area’s most polluted 15 cities are in India, the place industrial emissions, agricultural waste burning, cooking with strong fuels and cremation practices add to the air pollution burden.
India’s authorities banned coal burning for some commerical and industrial companies within the Nationwide Capital Area in January 2023 to attempt to cut back the smog. Nonetheless, the nation continues to construct its coal burning capability, with a plan so as to add 17 gigawatts of coal-based energy technology to come back on-line over the following 16 months.
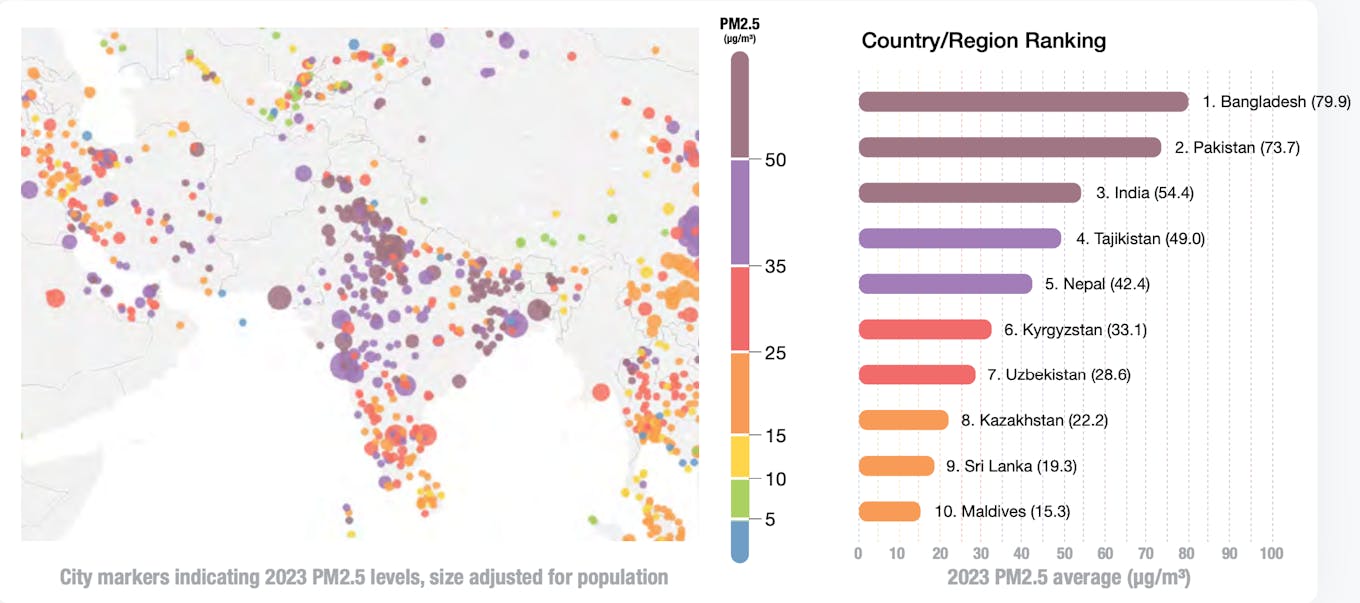
All 4 of probably the most polluted nations on the earth in 2023 had been in Central and South Asia; Bangladesh, India, Tajikistan, and Pakistan. Supply: IQAir


