Researchers in Indonesia have investigated how shading results could affect the efficiency ration of a PV system. Their evaluation additionally thought-about payback interval and return on funding.
Scientists from Indonesia have investigated the consequences of shading on a PV system’s efficiency ratio (PR) by contemplating completely different azimuth and photo voltaic module tilt angles.
The PR is a parameter that defines the connection between the precise and theoretical energy manufacturing of a PV system and is essentially unrelated to an set up’s location and orientation. This worth is used to grasp how effectively the PV system is working.
“Earlier research have largely targeted on how shadowing impacts a PV system’s vitality manufacturing,” the analysis mentioned.
Utilizing the PVsyst software program, the lecturers analyzed the shading results of a rooftop PV system put in on the administration constructing of the Polytechnic State of Ujung Pandang, which is positioned in Makassar, the biggest metropolis in Jap Indonesia.
“The PVsyst software program was utilized to guage the shading impact, loss diagram, and PR over the whole yr,” the analysis group mentioned. “The proposed scheme additionally examines the monetary evaluation of the proposed PV system, particularly, payback interval (PBP) and return on funding (ROI).”
The deliberate system was assumed to have two strings, with 9 PV modules in every string. Every panel had a nominal energy of 420 W in commonplace check circumstances, for a complete of seven.56 kW for the whole system of 18 modules. The researchers additionally assumed the system would promote surplus energy to the grid beneath a web metering regime.
The evaluation thought-about native world horizontal irradiation, horizontal diffuse irradiation, ambient temperature, world incident irradiation, and efficient world irradiation. All of those components had been then used to calculate the precise vitality produced by the PV array, vitality injected into the grid, and PR.
“Generally, there are solely two distinct seasons in Indonesia’s local weather: dry and wet, each of that are relative,” mentioned the scientists. “The dry season begins in April and lasts till September, with every of those two seasons lasting for six months. Then, on the finish of September till March, the wet season begins.”
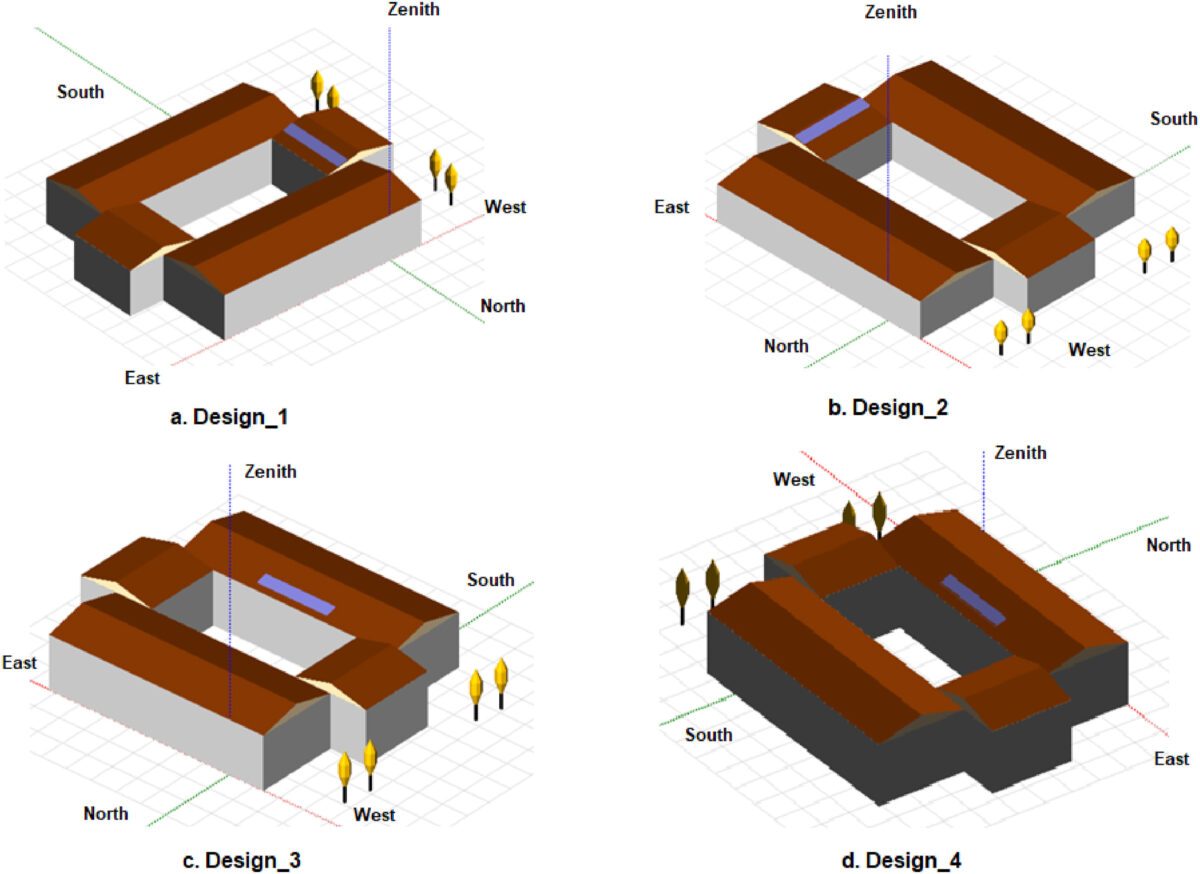
Based mostly on these circumstances, 4 situations had been examined: Design-1 with a tilt angle of 14 levels and an azimuth of -90 levels; Design-2 with a tilt angle of 13 levels and an azimuth of 90 levels; Design-3 with a tilt angle of 10 levels and an azimuth of 0 levels; and Design-4 with a tilt angle of 15 levels and an azimuth of 180 levels.
In line with the researchers, Design-3 achieved one of the best outcomes, with a PR of 0.817, PBP of seven.8 years, and ROI of 155.2%. However, Design-4 achieved the worst outcomes, with a PR of 0.815, PBP of 8.6 years, and ROI of 131.8%. Design-1 and Design-2 achieved comparable outcomes, with each having a PR of 0.816 and PBP of 8.2 years. Design-1 had an ROI of 145.2%, whereas Design-2 had 144.3%.
“Consequently, it is suggested to make the most of the Design-3 to realize one of the best PR and funding,” concluded the scientists.
Their findings had been introduced within the examine “Evaluating the shading impact of photovoltaic panels to optimize the efficiency ratio of a solar energy system,” revealed on Ends in Engineering. The analysis group was shaped by teachers from Indonesia’s Polytechnic State of Ujung Pandang and The College of Gadjah Mada.
This content material is protected by copyright and might not be reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and want to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.