A gaggle of researchers from Sweden has developed a brand new mannequin to search out the optimum tilt angle in PV installations positioned at excessive latitudes. The brand new strategy takes under consideration, amongst different components, the impact of transmittance change based mostly on snow.
Scientists from Sweden have developed a novel mannequin for optimum PV set up angles in chilly high-latitude areas. The mannequin makes use of climate massive knowledge and likewise accounts for the impact of transmittance change brought on by snow, which is calculated by bearing in mind snow depth, in addition to its melting charge.
“Snow-induced loss may be a small proportion for low/mid latitude,” the researchers stated. “Nonetheless, for the high-latitude areas the place the winter seasons are usually prolonged, the snow results play an necessary function in order that exclusion of snow results would considerably affect the reliability of the outcomes.”
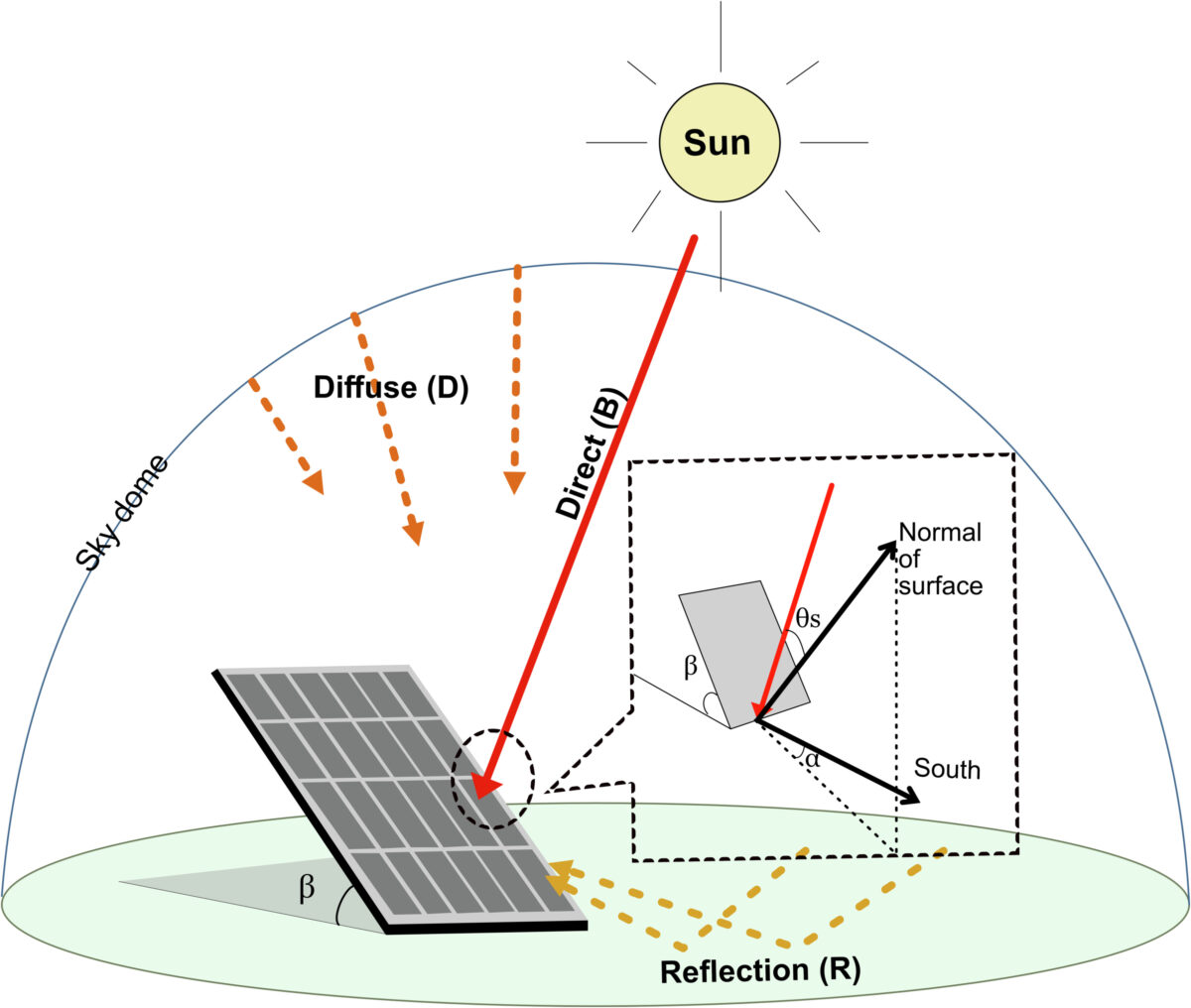
The novel methodology {couples} an optimum PV set up angle mannequin to maximise PV energy era with a simplified snow-PV yield mannequin (SPYM). The PV angle mannequin is executed with angles starting from 0 levels to 90 levels with 0.1-degree intervals, discovering the optimum place based mostly on whole international photo voltaic irradiation on the PV system, which is given by the sum of direct, diffuse, and reflection irradiation.
The adjusted irradiation is yielded from the SPYM mannequin, which relies on snow depth, air temperature, and irradiation. Whereas the temperature can predict whether or not the snow on the panel is melting or overlaying the module, the snow depth determines its transmittance.
“The calculation of this snow loss issue refers back to the transmittance mannequin from Perovich,” the teachers stated. “The transmittance drops sharply from 1 to 0.1 when snow depth will increase from 0 to 2 cm. Then, the lower turns into smoother, and the worth reaches 0.01 when the snow depth will increase to 12 cm. When the snow depth is thicker than 12 cm, the worth is assumed to be 0.”
Picture: Utilized Power, KTH Royal Institute of Expertise, CC BY 4.0 DEED
Following the event of the mannequin, the scientists used Solcast historic meteorological knowledge for 2012-2021 for the Swedish metropolis of Hammarby Sjöstad as enter. Optimum calculations had been made for one 12 months, 5 years, and ten years. Of their case research, they assumed PV modules with 19.2% effectivity and an output of 430 MW.
Then, they in contrast and used their novel mannequin for 3 eventualities. The primary case was a base case with no snow situations, contemplating solely historic irradiation and temperature knowledge. Within the second state of affairs, snow results had been calculated with the belief that it melts after 12 hours. The final state of affairs assumed elimination brokers, which shortened the snow elimination time to at least one hour. All the outcomes had been in comparison with the business insulation angle of 15 levels and the geometric angle for Sweden, 40.7 levels.
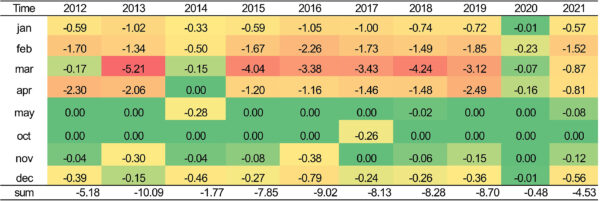
“The PV system with the annual optimum angle outperforms the one with a business angle, leading to an approximate 4.8% improve in energy era,” the analysis group said. “The optimum PV set up angle decreases when contemplating snow situations, with the distinction depending on native climate situations annually, reaching as much as 7.8 levels.”
As well as, the scientific group discovered that snow situations lowered energy era situations by 14.7%. In addition they discovered that making use of elimination brokers can enhance PV efficiency by 0.1%–2.3%.
Their findings had been introduced in “A brand new optimum PV set up angle mannequin in high-latitude chilly areas based mostly on historic climate massive knowledge,” revealed on Utilized Power. The analysis was performed by teachers from Sweden’s KTH Royal Institute of Expertise and the Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute.
This content material is protected by copyright and is probably not reused. If you wish to cooperate with us and want to reuse a few of our content material, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.