The seven European nations that make up the Pentalateral Vitality Discussion board—Austria, Belgium, France, Germany, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and Switzerland—will attempt for the decarbonization of their interconnected electrical energy system by 2035.
The nations, which type the Pentalateral Vitality Discussion board—a 2005-convened voluntary framework for regional vitality cooperation—in a joint assertion on Dec. 18 formally concluded, “well timed decarbonization of the electrical energy system is a prerequisite to permit for full decarbonization of our societies by 2050, and that collective motion in our area permits to handle this problem in a extra environment friendly and efficient method.”
Goal Reliant on Key Guiding Ideas
The nations, which, aside from Switzerland, are all a part of the European Union (EU), additionally agreed on a set of guiding ideas. Amongst them is that they are going to apply an “vitality effectivity first” precept to mitigate an anticipated enhance in energy demand. The Pentalateral Vitality Discussion board additionally acknowledged a necessity for accelerated deployment of renewables, coordinated vitality system planning, and adaptability as a “prerequisite.”
Different guiding ideas embrace acknowledging a “pivotal position for molecules,” akin to hydrogen, together with their “basic position in stabilizing a decarbonized electrical energy system.” Infrastructure improvement, together with grid modernization and reinforcement, will even be crucial, the discussion board stated.
Lastly, “We acknowledge the need of a future-proof market design. This design ought to incentivize crucial investments in renewable technology, flexibility, storage and transmission infrastructure and permit for environment friendly dispatch, and guarantee useful resource and transmission adequacy for a sustainable and resilient vitality future,” it stated.
An Vital Stepping Stone Towards Full Decarbonization by 2050
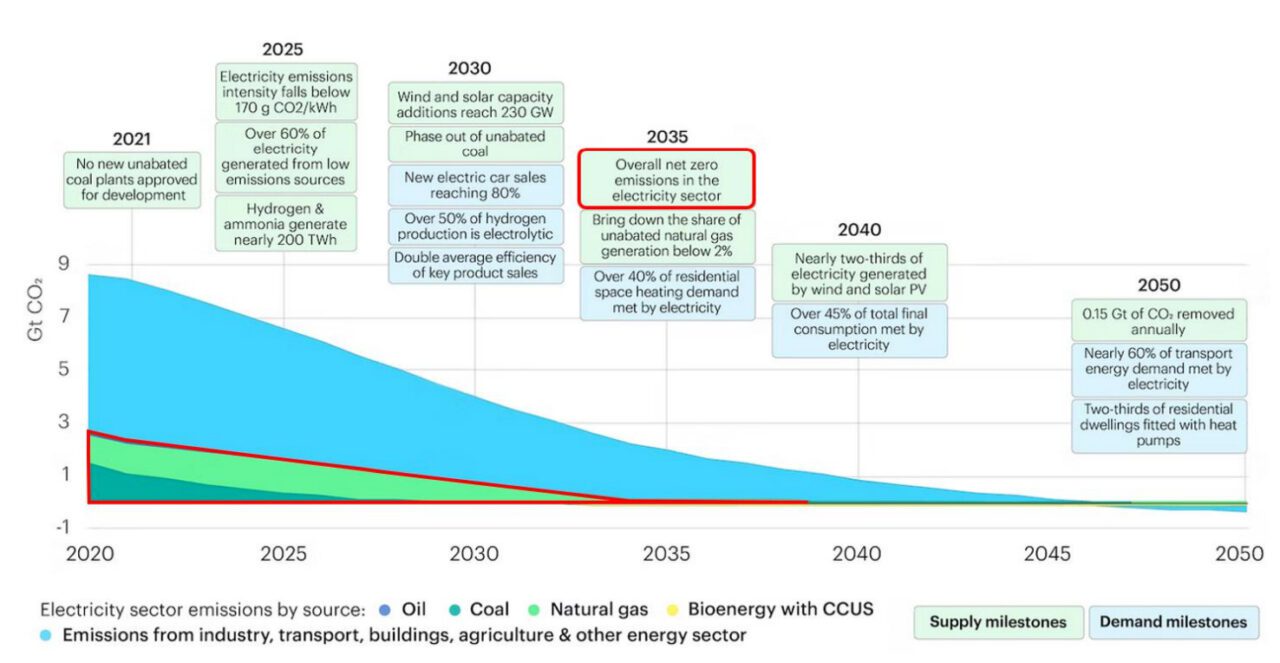
The assertion on Monday stems from a 2021-issued dedication by discussion board ministers to succeed in full decarbonization of the electrical energy system by 2050. “A number of research to analyze potential futures of our vitality system” point out that decarbonization of the nations’ electrical energy programs by 2035 can be an necessary step towards attaining that purpose.
A current research commissioned by the Benelux Basic Secretariat on the discussion board’s behalf analyzed a number of developments gleaned from present situation assessments and technical studies, and it lays out 12 “convictions.” Foremost amongst them is that the facility sector will have to be decarbonized as “early as potential, ideally by 2035,” with carbon intensities beneath 50 grams/kWh. The 2035 date is predicated on an Worldwide Vitality Company (IEA) net-zero situation rolled out in 2021, and it was additionally endorsed by the G7 at their 2022 summer time summit. The U.S., notably, has set the same purpose of 100% carbon pollution-free electrical energy by 2035.
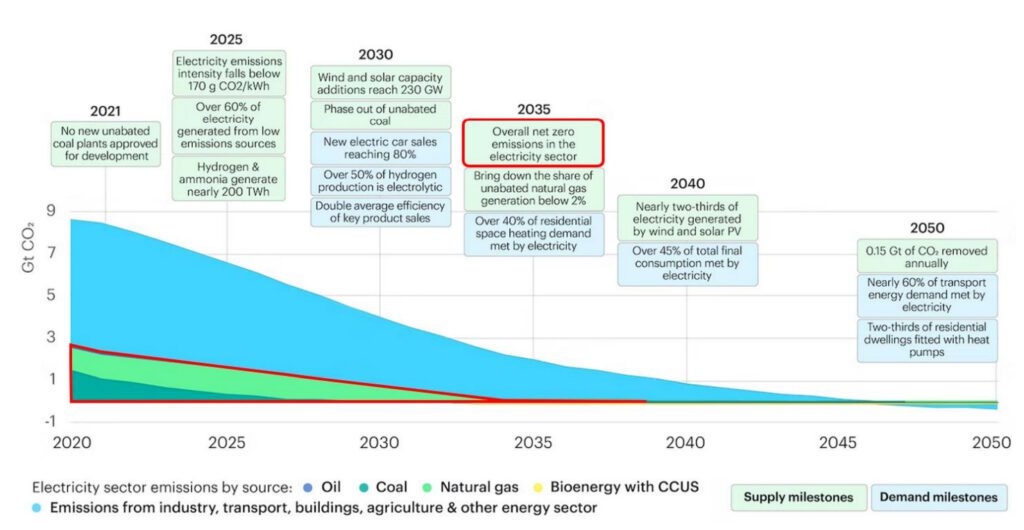
Nonetheless, the report additionally underscores how difficult the purpose could also be to realize. Whereas low-carbon applied sciences can be crucial, the decarbonization of quite a few hard-to-abate sectors (akin to trade, transport, and buildings) will depend upon energy sector decarbonization, through direct (direct use of energy) and oblique electrification (changing energy into hydrogen or different artificial derivatives). “This means a big growth of the facility sector,” the report suggests. The rise in home energy demand might double in some Penta nations by 2050, it notes.
Renewables can be a “important pillar” to realize the goal. “The sum of photo voltaic and wind capacities throughout probably the most bold eventualities mounts as much as 1,100 GW by 2050 versus 180 GW at this time—that may be a issue of 6,” the report notes. “But, the rollout of renewable installations must strongly pace up: annual photo voltaic PV installations have to double within the present decade in comparison with the earlier one, and they should double once more after 2030. Quicker allowing procedures, amongst different measures, will assist to unlock these investments,” it says.
In the long term, necessary quantities of renewable electrical energy are foreseen to be imported notably from the Baltic Sea, Southern Europe, and probably the MENA area, requiring further cross-border capacities.” In lots of eventualities, “electrical energy imports cowl between 10% and 30%, and going as much as 50% in chosen eventualities, of whole energy demand by 2050. Extra inner and cross-border capacities are wanted to allow such import volumes from different European nations,” it notes.
Nonetheless, the necessity for and position of “different extra immature low carbon energy technology applied sciences,” akin to small modular reactors, tidal and wave energy manufacturing, and ultra-deep geothermal and nuclear fusion, stay unsure. “Uncertainty additionally stays concerning the import ratio between electrical energy and decarbonized molecules, in addition to the supply nations outdoors Penta and probably over-seas exporting the hydrogen (or hydrogen derivatives),” it says.
An Ambition Fogged by Uncertainties
Uncertainties are additionally pegged to energy demand. Direct electrification might end in a major enhance in demand of as much as 40% in 2030 and greater than double by 2050. Whereas the “vitality effectivity first” precedence might “launch strain” on the facility system, the magnitude of accelerating constructing renovations, for instance, is topic to uncertainty on account of a scarcity of expert labor and persisting owner-tenant dilemmas, the report notes. “The feasibility and effectiveness of a round and extra vitality environment friendly economic system can also be questionable, notably as a result of danger of a rebound impact following vitality effectivity enhancements,” it says.
Energy grid capacities should additionally in the end accommodate new demand. “Inner electrical energy transmission and distribution networks face unprecedented challenges, most notably a major rise in related renewable capacities and demand volumes,” the report says. “In some eventualities, [renewable energy source (RES)] capacities related to distribution grids enhance by an element of 5 to 7 in comparison with present ranges, demand volumes by an element of two (with peak hundreds probably that includes an much more necessary rise in case of suboptimal load profiles).”
Together with lowering system inertia, grid growing old, and rising transit flows, the prospect of recent variable sources outcomes “in a powerful want to extend energy grid capacities, by way of a wiser and extra environment friendly operation of present belongings (e.g., through dynamic line ranking, phase-shift transformers, energy electronics), and thru grid reinforcement,” it notes. “Annual distribution grid prices are anticipated to extend by 25% to 100% till 2050; annual prices for transmission grids might rise much more importantly by as much as an element of 4.”
The Pentalateral Vitality Discussion board has underscored a necessity for a “coordinated method to vitality system planning.” A key goal needs to be to “identify the optimum trade-off between the exploitation of high-performance RES potentials, electrolyzer siting, and optimized energy/fuel/hydrogen grid adaptation (administration, repurposing, reinforcement),” the report says. “It requires a major effort of coordination (i.e., transaction prices), however permits for cost-efficient infrastructure deployment and avoids stranded belongings.”
Flexibility will little question be key to enabling a decarbonized energy sector. “Every day flexibility wants are anticipated to rise by an element of three to 4 on the Penta-level, and greater than an element of 5 in chosen Penta member nations till 2050. Seasonal flexibility wants face a much less pronounced however nonetheless essential enhance (as photo voltaic and wind technology function seasonal patterns, and heating is additional electrified),” the report says. Nonetheless, uncertainty stays “on the magnitude of participation of renewable or low-carbon fuel within the energy sector, notably concerning the position of biomethane and hydrogen in peak energy technology, and the necessity for hydrogen or its derivatives as seasonal energy storage.”
Regional cooperation and enhanced cross-border interconnection “might soften” the huge enhance in flexibility wants, the report concludes. “By ‘merely’ interconnecting the Penta market space, demand and RES variation flattens out considerably, implying a ten% discount in flexibility wants,” it says. “That’s, regional cooperation lowers prices and facilitates RES system integration.”
Reaching all of this will even be contingent on how efficiently the area facilitates a “future-proof electrical energy market design.” The report lays out a number of suggestions. Market areas needs to be additional interlinked “by way of bolstered cross-border interconnection capacities but in addition through market integration, cross-border cooperation to share reserve capability and internet balancing, the joint improvement of offshore wind vitality parks, so-called hybrid initiatives,” it suggests. Investments and incentives, by way of capability remuneration mechanisms, will even be required. “The participation of all flexibility sources needs to be enabled, and the potential reconfiguration of bidding zones may very well be investigated,” it says.
—Sonal Patel is a POWER senior affiliate editor (@sonalcpatel, @POWERmagazine).