The ability sector’s relentless pursuit of an more and more linked energy paradigm amid an escalating cyber risk panorama calls for an pressing, multifaceted technique for cybersecurity. Lately, the sector has launched into progressive strategies to sort out inherent challenges in its evolving quest for a strong cybersecurity posture.
In 2022, a 3rd get together alerted industrial management methods (ICS) agency Dragos it had recognized a brand new assortment of malware, PIPEDREAM, that fostered a “reusable cross-industry functionality” that would unleash disruptive and even damaging results on ICS/operational know-how (OT) gear. As Dragos CEO Robert Lee defined to Congress in March 2023, “Years in the past, I usually [said] that I used to be not fearful in regards to the threats of at this time as a result of our infrastructure homeowners and operators had centered a lot on reliability and security that it naturally helped cybersecurity.” However PIPEDREAM, distinct for its functionality to take advantage of “homogenous infrastructure,” shocked him.
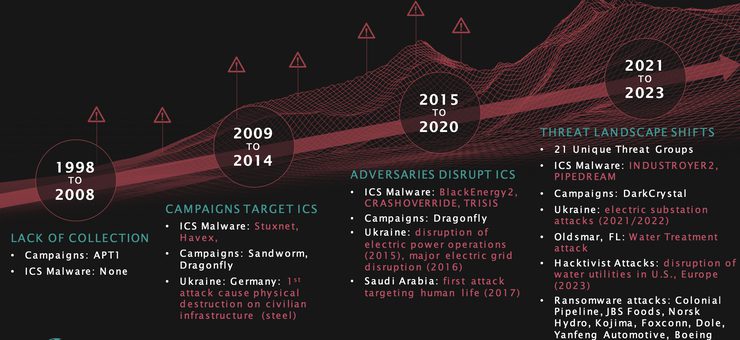
“Primarily based on Dragos’ evaluation, PIPEDREAM was initially focused towards power belongings equivalent to liquid pure gasoline and electrical transmission gear,” he famous, “however it could possibly work on virtually all OT environments, starting from the heating, air flow, and cooling gear in knowledge facilities to manage methods utilized in next-generation army and weapons methods.” And whereas PIPEDREAM was considered one of many ICS-specific malwares—following STUXNET, AURORA, HAVEX, BLACKENERGY2, CRASHOVERRIDE/INDUSTROYER, TRISIS/TRITON, and INDUSTROYER2 (Determine 1)—it offered “the primary life like cyber functionality that may considerably disrupt important infrastructure domestically,” he stated. “It’s not functionality you may merely patch away or in any other case stop. As soon as it’s in a goal’s networks, it’s a dependable instrument for an assault because it takes benefit of the native performance and customary software program now deployed throughout infrastructure websites.”
PIPEDREAM’s identification led Dragos and its companion to the Nationwide Safety Company (NSA), Federal Bureau of Investigations (FBI), Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Company (CISA), and Division of Vitality (DOE), and beneath “one of the crucial important public-private partnership wins of all time in cybersecurity,” the collaborative effort recognized, analyzed, and in the end reported PIPEDREAM to the broader infrastructure neighborhood earlier than PIPEDREAM may make an affect, Lee stated. Whereas its proactive containment represents a victory, the specter of the insidious malware that may unleash probably huge repercussions stays important.
One cause is that since 2015, when a cyberattack prompted energy outages in Ukraine, the ability sector has dramatically ramped up its cybersecurity posture. However adversaries have been relentless. “In 2017, the first-ever cyberattack that focused human life immediately occurred in a Saudi Arabian petrochemical facility by focusing on an OT system,” Lee famous. “Throughout 2018 to 2021, there have been over a dozen new state actor cyber groups that began focusing on industrial firms immediately.”
Assaults have highlighted vulnerabilities in all components of the {industry}. The 2020 SolarWinds SUNBURST assault, spearheaded by the Russian Overseas Intelligence Service, uncovered pc networks worldwide, highlighting vulnerabilities in provider and producer networks. (Whereas SolarWinds initially reported 18,000 clients may probably have been weak to SUNBURST, the agency estimates the precise variety of clients hacked via SUNBURST to be fewer than 100.)
Ransomware operations are in the meantime ramping up, reviews safety agency Resecurity. Whereas the power {industry} has seen a “transient, sectoral ‘ceasefire’ following the 2021 Colonial Pipeline ransomware assault, cybercriminals are as soon as once more honing in on energy-industry targets,” it warned in November. “Within the wake of the MOVEit Switch supply-chain extortion marketing campaign, which has claimed over 2,180 victims thus far, 2023 may very well go down in historical past as probably the most worthwhile yr ever for ransomware actors. The broader development driving the ransomware {industry}’s rising ROI [return on investment] is the return of ‘massive sport looking,’ or the focusing on of enormous organizations,” it stated. Operators are actually focusing on nuclear, and oil and gasoline companies, and “will proceed to extend their extortion demand past $7 million, weaponizing their essentiality to CI [critical infrastructure] operations,” it stated.
A Collective Push Towards Resilience
For the ability sector, cyber threats stay top-of-mind, however its quest for good cybersecurity posture has advanced into a vital threat administration technique with a number of new drivers. For one, important safety dangers are related to the altering useful resource combine. The grid transformation “is increasing the prevailing assault floor because of using rising applied sciences, further communications, and industrial controls in addition to distant management capabilities,” explains the North American Electrical Reliability Corp. (NERC), a quasi-governmental compliance enforcement authority.
Fashionable cybersecurity, which incorporates a number of safety ideas and ideas, usually contains a defense-in-depth philosophy, however these weren’t traditionally built-in into the planning, design, and operation of the grid’s OT methods, NERC notes. As a part of their embrace of digitalization, energy firms are more and more connecting the OT atmosphere to exterior networks via the incorporation of clever units able to web protocol (IP) communications. “These channels present alternatives for adversaries to take advantage of latent vulnerabilities inside the present system, as cybersecurity was not a part of the design equation for legacy gear, software program, and networks. The introduction of recent applied sciences and new kinds of entities getting into electrical energy markets additionally current new cyber-attack vectors,” it added.
In North America, energy entities abide by NERC Crucial Infrastructure Safety (NERC CIP) requirements, which have set necessities for cybersecurity administration and management, personnel coaching, incident reporting, response planning, restoration plans for important cyber belongings, and safety controls for grid know-how and product suppliers. The European Union, in the meantime, in October 2023, modernized its 2016 Community and Data Directive (NIS). The replace broadens the scope of important entities to recharging level operators and numerous electrical energy market members, and it reinforces cybersecurity necessities alongside their provide chain.
Energy sector cybersecurity posture has additionally been guided by voluntary cybersecurity frameworks, together with from the DOE and the Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Know-how (NIST), and public-private collaborations, equivalent to an effort led by the Electrical energy Data Sharing and Evaluation Heart (E-ISAC). One instance is the Cybersecurity Threat Data Sharing Program (CRISP), which facilitates the well timed bi-directional sharing of unclassified and labeled risk data, and growth of situational consciousness instruments. CRISP members presently present energy to greater than 75% of U.S. clients, the DOE stated.
Nevertheless, the ability sector’s cybersecurity crucial additionally largely responds to shareholder issues about company dangers posed by cybersecurity. In March 2022, the U.S. enacted the Cyber Incident Reporting for Crucial Infrastructure Act, inserting a reporting obligation on firms in some important infrastructure sectors, together with power and nuclear reactors. And in July 2023, the U.S. Securities and Change Fee (SEC) finalized a rule that mandates disclosure concerning cybersecurity threat administration, technique, governance, and incident reporting for publicly traded firms. Future guidelines could hinge on the White Home’s March 2023 rollout of a Nationwide Cybersecurity Technique, which envisions “elementary shifts” in how the U.S. allocates roles, tasks, and sources within the our on-line world.
Business-Led Innovation
“Laws, if achieved accurately, are good and required to set a baseline,” famous Patrik Boo, portfolio supervisor of Cyber Safety Companies at ABB. “The chance, when laws are usually not achieved nicely, is that they set a minimal degree,” he famous. Business seems to grasp this. Regardless of pressures, it’s at this time leveraging a legacy in innovation and has launched into exploring new instruments to boost cybersecurity together with effectivity.
Some firms are wanting into integrating synthetic intelligence (AI) to boost and streamline cybersecurity. AI for cybersecurity providings additionally seems to be ramping up. Know-how agency NVIDIA lately rolled out Morpheus, an open utility framework that “allows cybersecurity builders to create optimized AI pipelines for filtering, processing, and classifying massive volumes of real-time knowledge,” It primarily brings a “new degree of safety to the info heart, cloud, and edge,” through the use of AI to “determine, seize, and act on threats and anomalies that have been beforehand unimaginable to determine.” One attribute, for instance, makes use of digital fingerprinting of the AI workflow to “uniquely fingerprint each person, service, account, and machine throughout the community—using unsupervised studying to flag when exercise patterns shift.”
Efforts are additionally progressing to combine blockchain—greatest identified for securing digital forex funds—with cybersecurity. A venture beneath Oak Ridge Nationwide Laboratory’s Darknet initiative had developed a framework to detect uncommon exercise, together with knowledge manipulation, spoofing, and illicit modifications to system settings. “Cyber dangers have elevated with two-way communication between grid energy electronics gear and new edge units starting from photo voltaic panels to electrical automotive chargers and clever house electronics. These actions may set off cascading energy outages as breakers are tripped by safety units,” ORNL famous. The framework proposes a “completely new functionality” to answer anomalies quickly,” it stated. “In the long term, we may extra rapidly determine an unauthorized system change, discover its supply, and supply extra reliable failure evaluation. The aim is to restrict the harm attributable to a cyberattack or gear failure.”
The DOE’s Workplace of Cybersecurity, Vitality Safety, and Emergency Response (CESER) is spearheading a number of notable partnerships with {industry}, together with funding initiatives, aimed toward enhancing energy sector cybersecurity. A notable program is the Cyber Testing for Resilient Industrial Management Programs (CyTRICS) program at Idaho Nationwide Laboratory, which exams important system elements to determine cyber vulnerabilities earlier than they’re exploited. The hassle is geared to enhance the safety of ICS and software program provide chains.
“DOE connects gear producers, distributors, and utilities with state-of-the-art, intelligence-informed analytic capabilities at its Nationwide Laboratories the place they take a look at operational know-how elements voluntarily submitted by the collaborating firms,” CESER famous. In January, nuclear large Westinghouse joined 4 personal sector firms, GE Vernova, Hitachi Vitality, Schneider Electrical, and Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories in this system. Westinghouse will take a look at for potential cyber vulnerabilities in one of many firm’s instrumentation and management methods used for nuclear functions.
CESER can be spearheading different noteworthy packages. It lately launched the Renewable Vitality and Storage Cybersecurity Analysis (RESCue) initiative, which seeks to handle cybersecurity issues in hybrid power methods, together with wind, photo voltaic, and power storage. As well as, it lately launched $100 million in funding to discover cyber-resilient design frameworks for hybrid renewable methods, instruments for forensic evaluation, applied sciences to determine and mitigate cyber threats to inverter-based sources (IBRs) and power storage, safe communications options for distributed power sources (DERs), and cybersecurity enhancements for digital energy crops.
The Daring Prospect of Safety Integration
Business can be individually working with NERC to discover a “safety integration,” which makes an attempt to set down a extra built-in strategy to include cyber and bodily safety into planning, design, and the operational phases of belongings on the majority energy system. Current efforts, for instance, embrace gear requirements and system certification for behind-the-meter DERs, cyber-informed transmission planning approaches, and suggestions to handle cyber threats dealing with IBR distributors, homeowners, operators, and aggregators.
To handle safety dangers within the provide chain, the ability sector is in the meantime championing Software program Payments of Supplies (SBOMs). SBOMs are primarily an “IT [information technology] listing of components in software program,” Alex Santos, co-founder and CEO of Fortress Data Safety, defined to POWER. “Software program will not be coded anymore—it’s assembled like Lego in blocks” from catalogs. Blocks, for instance, comprise a database or a login display, he stated. “So, the SBOM is an ingredient listing of the Lego items in our software program.”
Fortress lately known as consideration to insidious cybersecurity points that lurk in software program merchandise used to handle the U.S. energy grid. In a report, the agency stated that an estimated 90% of software program merchandise, together with IT merchandise, that are utilized for community administration, in addition to OT merchandise, that are used to watch and management bodily processes and gear, include code “contributions” from Russian or Chinese language builders. Santos famous federal entities just like the CISA have supported SBOMs as a important instrument to stop cyber-attacks, and the federal government has explored mandating SBOMs for software program makers. “If the {industry} takes steps to require SBOMs and attestation kinds voluntarily, the much less the federal government must mandate them,” he stated.
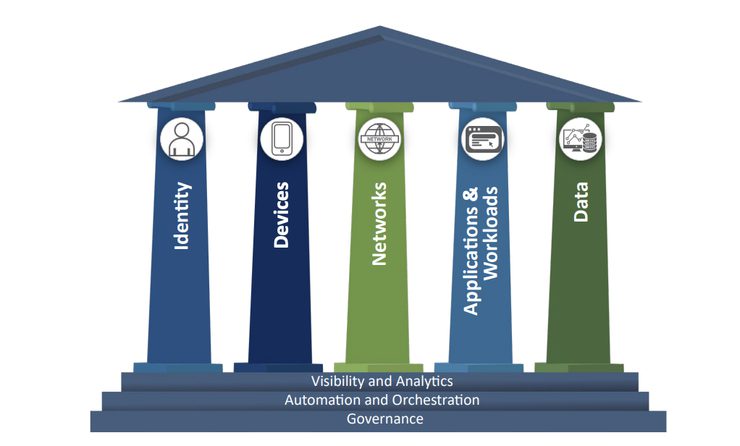
One more rising industry-championed attribute is the “zero-trust” (ZT) precept. Looking for to proactively handle threats to OT know-how, together with ransomware and malware instruments like PIPEDREAM, ZT is a set of ideas (Determine 2) that builds upon and enhances historic controls and perimeter-based safety fashions—versus tearing them down. “Business must proceed to develop gear and software program in addition to individuals, processes, insurance policies, and governance able to delivering on ZT ideas,” NERC stated. “Entities ought to spend money on workers coaching for ZT, develop OT safety packages, design roadmaps primarily based on a ZT maturity mannequin for the event of ZT structure (ZTA) on the proper tempo for his or her group.” ZTA, nonetheless, might be a long-term effort. NERC suggests operators ought to usually start by implementing it of their IT environments, specializing in IT/OT demilitarized zones (DMZs) and operational management facilities.
ZTA, nonetheless, might be a long-term effort. NERC suggests operators ought to usually start by implementing it of their IT environments, specializing in IT/OT demilitarized zones (DMZs) and operational management facilities. These areas, characterised by fashionable, versatile digital platforms and superior community infrastructures with shorter refresh cycles, supply probably the most important alternatives for ZTA deployment, offering a good value/profit ratio by addressing a broad assault floor and minimizing potential disruptions, it stated. The hassle ought to be pursued “incrementally” and in collaboration with OT integrators and distributors. “OT networks and legacy units could create constraints that require hybrid approaches to unravel,” it famous. “No single product or instrument on {the marketplace} supplies a whole ZTA, and organizations could have already got infrastructure and controls in place that qualify as elements of a ZTA.”
Pervading Challenges
Regardless of these measures, consultants counsel extra will must be achieved, and a number of other challenges lie forward. Probably the most obtrusive difficulty stays an organizational difficulty, the place “engineers and managers who ‘personal’ the ability plant and substation gear are typically not a part of a cybersecurity program,” stated Joseph Weiss, a registered skilled engineer, who’s managing director of ISA99, an Worldwide Society of Automation (ISA) requirements committee that produced and continues to develop the ISA/IEC (Worldwide Electrotechnical Fee) 62443 sequence of requirements and technical reviews. ISA/IEC 62443 supplies a framework for guaranteeing the safe operation of OT methods used throughout numerous sectors. A key cause is that “cybersecurity is being addressed as a community drawback,” Weiss confused. He famous the mismatch is longstanding and has its roots within the early 2000s, when firms started shifting their cybersecurity from operational organizations to IT.
At the moment, Weiss stated there isn’t a cybersecurity, authentication, cyber forensics, or cybersecurity coaching for management system area units equivalent to course of sensors, actuators, and drives. The dire hole poses a severe cybersecurity oversight with potential impacts to reliability and course of security, he famous. Weiss warned that present laws and approaches aren’t proving efficient as a result of “present know-how will not be figuring out, stopping, or mitigating management system cyber incidents. There have been tons of of energy plant and substation cyber incidents which have shut down amenities or broken gear however are exterior the scope of cyber safety laws,” he stated.
Analysis and advisory agency Gartner identified different pervading challenges, together with difficulties in fulfilling a requirement for safety expertise (Determine 3). “The worldwide cybersecurity expertise scarcity is a perennial difficulty,” it famous. Within the U.S. alone, there are solely sufficient certified cybersecurity professionals to fulfill 70% of present demand—an all-time low over the previous decade. Sadly, labor market supply-and-demand points can’t be solved by particular person safety and threat administration (SRM) leaders,” it stated. “What will be solved is an rising expertise hole. But cybersecurity leaders proceed to rent for legacy roles and expertise,” it stated.
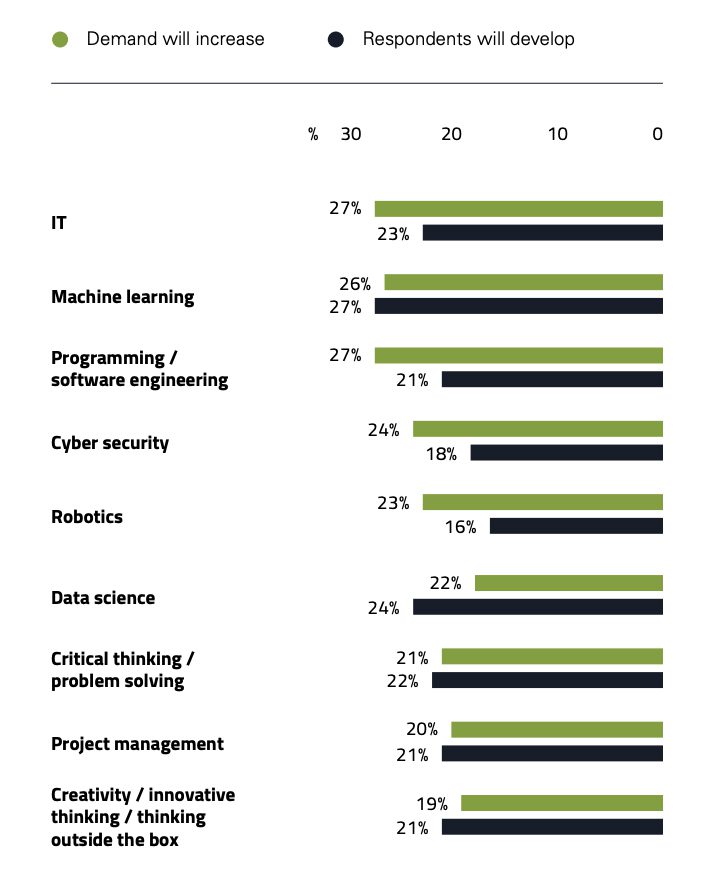
The talents that cybersecurity groups want are altering drastically, given a convergence of megatrends. These embrace cloud adoption, the fast rise of generative AI, an working mannequin transformation requiring cybersecurity professionals to more and more work with and thru enterprise companions, and vendor consolidation. The risk panorama now additionally encompasses cyber-physical methods, distant work, and generative AI, it famous. “SRM leaders should reskill their groups by retraining present expertise and hiring new expertise with new profiles,” Gartner stated.
These new calls for arrive with new scrutiny about company spending because the {industry} grapples with inflationary pressures and different {industry} disruptions. In response to a benchmarking collaboration between safety practitioners, IANS Analysis, and human sources agency Artico Search learning safety budgets over 2023, cybersecurity budgets grew solely 6%, “a modest determine following double-digit will increase in 2020 and 2021,” although practically a 3rd of the 550 safety executives it surveyed reported flat or declining budgets.
ABB’s Boo recommended that “whereas many energy firms’ initiatives are spearheaded by one or two reality fighters—those that actually dwell for cybersecurity though it might not be their devoted position—in addition they depend on exterior assist for numerous causes. It’s extraordinarily useful to them as a result of they get all that mixed expertise from that exterior consultancy or useful resource as part of their group,” Boo stated. Third-party consultants like ABB, he famous, are sometimes sensible and pragmatic. “We make the most of {industry} requirements, equivalent to IEC 62443, to ascertain a strong community structure and foundational cybersecurity, which will be expanded upon with further cybersecurity measures as wanted.” As well as, third-party companies are usually conscious of rising applied sciences, due to this fact, they will information clients via suggestions, he stated. “Increasingly of our clients I discuss to have truly achieved spectacular issues and are taking cybersecurity severely, however I additionally concern that there’s lots on the market that would use somewhat little bit of a lift.”
—Sonal Patel is a POWER senior affiliate editor (@sonalcpatel, @POWERmagazine).
Correction (Feb. 20): This text erroneously reported the 2020 SolarWinds assault uncovered as many as 16,000 pc networks worldwide. SolarWinds’ up to date estimates counsel fewer than 100 clients have been hacked via SUNBURST.


