The U.S. Environmental Safety Company (EPA) in February issued a closing rule imposing tighter restrictions on tremendous particulate matter (PM2.5) or soot.
The closing rule, issued on Feb. 7, strengthens the nation’s Nationwide Ambient Air High quality Requirements (NAAQS) by reducing the extent of the first (health-based) annual PM2.5 customary from 12.0 micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m3) to 9.0 µg/m3. The EPA, nevertheless, retained the first 24-hour PM2.5 customary at its present degree of 35 µg/m3 and the first 24-hour PM10 (coarse particle) customary at its present degree of 150 µg/m3. It additionally concluded secondary PM requirements—requirements to guard public welfare—present a adequate safeguard, and it decided no adjustments had been essential “presently.”
A Tighter Rule for Regional Impression
“This closing rule doesn’t make any air high quality attainment/nonattainment designations,” the EPA famous. “Per Clear Air Act timelines, EPA is required to designate areas as attainment or nonattainment inside 2 years of the ultimate rule.” Nevertheless, most counties with screens already meet the strengthened PM2.5 customary, it mentioned. In 2032, solely round 52 counties—23 in California—wouldn’t meet the brand new customary, the company estimated.
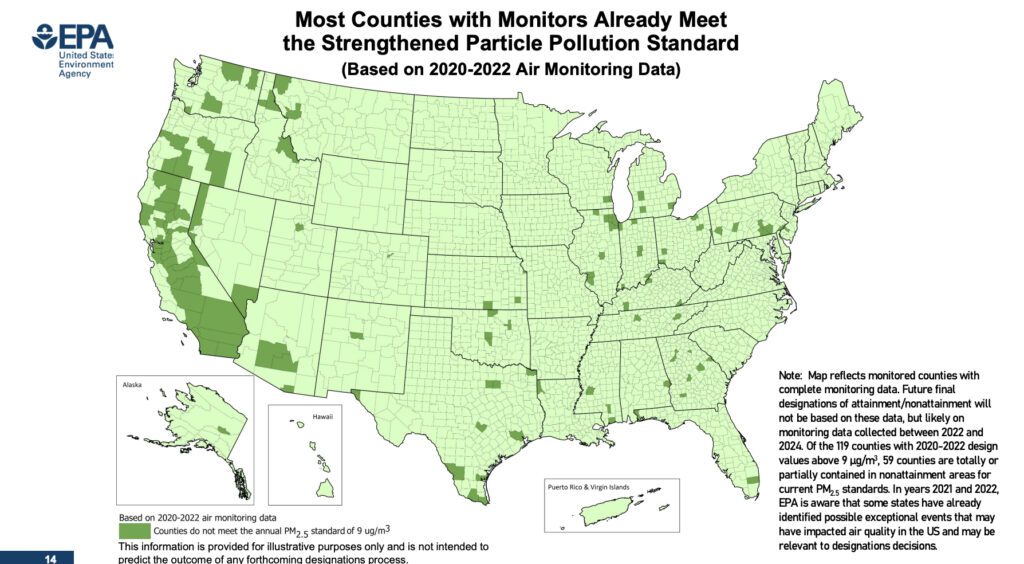
Areas with air high quality that don’t meet the brand new customary can be designated by the EPA, seemingly in 2026, as “nonattainment.” That may set off an obligation for states to revise their state implementation plans (SIPs) to acquire additional emission reductions to make sure that the brand new customary can be met. States are anticipated to submit SIP revisions inside three years after a closing NAAQS.
The ability business suggests areas round some producing amenities could also be deemed nonattainment, which may topic them to extra air pollution controls or operational constraints. Nevertheless, as a result of SIP revisions by affected states will take time to finish, it’s unclear how SIP necessities will have an effect on regional energy era.
‘New Science on Harms’
The company mentioned it promulgated the ultimate rule “to replicate new science on harms attributable to particle air pollution.” The rule takes into consideration “the out there scientific proof, recommendation from the Clear Air Scientific Advisory Committee (CASAC), and practically 700,000 public feedback.” The stronger PM NAAQS “will advance environmental justice by resulting in reductions in particle air pollution, which disproportionately burdens communities of coloration and different weak communities,” it mentioned.
By legislation, the EPA can’t think about prices in setting or revising NAAQS. “Nevertheless, to tell the general public, EPA analyzes the advantages and prices of implementing the requirements as required by Government Orders 14094, 12866 and 13563 and steerage from the White Home Workplace of Administration and Finances,” the company famous. The EPA’s Regulatory Impression Evaluation suggests estimated prices related to management methods for the revised requirements will quantity to $594 million in 2032 (2017$, 7% rate of interest). Its estimated monetized advantages related to these management methods are roughly $20 billion and $42 billion in 2032 (2017$, based mostly on an actual low cost charge of seven%).
Falling Energy Sector Air Pollutant Emissions
The Clear Air Act (CAA) requires the EPA to set two kinds of NAAQS for PM: major requirements to guard public well being “with an sufficient margin of security,” and secondary requirements to guard public welfare from each recognized and anticipated adversarial results, together with from haze in cities and nationwide parks. Beneath the legislation, the EPA should evaluation the NAAQS each 5 years to find out whether or not they need to be retained or revised.
Since 1971, the company has now regulated PM air pollution 4 instances—in 1987, 1997, 2006, 2012, and 2024. In 2012, the Obama administration tightened the first customary for PM2.5 to 12.0 micrograms per cubic meter (µg/m3) from the prevailing 1997-set annual customary of 15.0 μg/m3, nevertheless it retained the 2006-issued 24-hour major tremendous particle customary of 35 μg/m3. The Trump administration in 2020 retained its current NAAQS for each tremendous and coarse PM (PM2.5 and PM10).
High-quality particles (PM2.5), that are 2.5 micrometers in diameter and smaller, are emitted by a wide range of sources, together with smokestacks, automobiles, and fires, however additionally they kind when gases emitted by energy crops, different industrial processes, and gasoline and diesel engines react within the ambiance. PM2.5 precursor gases embody sulfur dioxide (SO2), nitrogen oxides (NOX), risky natural compounds, and ammonia.
Coarse particles (PM10), which have diameters between 2.5 and 10 micrometers, embody highway mud kicked up by site visitors, some agricultural operations, development and demolition operations, industrial processes, and biomass combustion.
Based on the EPA, PM2.5 concentrations have largely decreased, akin to reductions in SO2 emissions from giant energy crops within the Jap U.S. and NOX reductions from cell sources and energy crops.
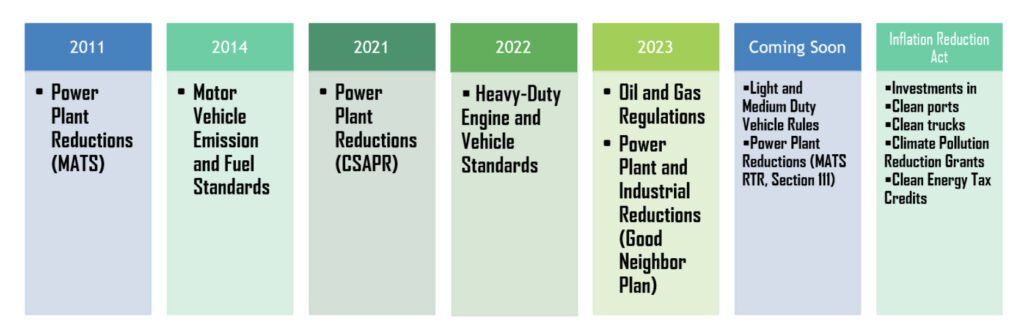
The EPA famous its rule thought-about a number of different rules. These embody the closing Good Neighbor Plan for the 2015 Ozone NAAQS (2023), the revised Cross-State Air Air pollution Rule Replace (2021), Requirements of Efficiency for Greenhouse Gasoline Emissions from New, Modified, and Reconstructed Stationary Sources (2015), the Mercury and Air Toxics Rule (2011), and provisions of tax incentives within the Inflation Discount Act of 2022 (IRA).
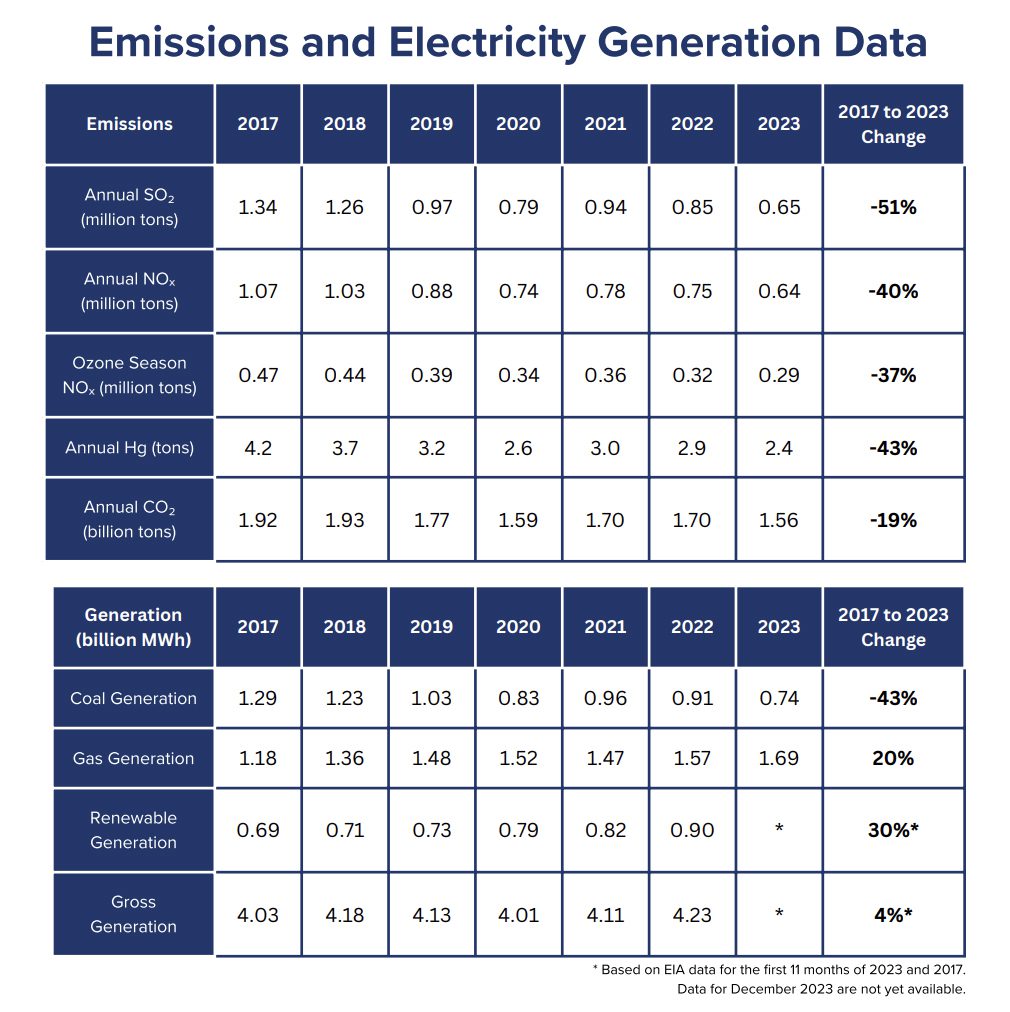
On Feb. 15, the EPA prompt the ability business has made dramatic progress in decreasing air pollution and enhancing air high quality. The company’s annual knowledge on 2023 emissions from energy crops within the decrease 48 states reveals that in comparison with 2022, 2023 knowledge present a 15% lower in NOX emissions, a 24% lower in SO2 emissions, a 7% lower in carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, and a 17% lower in mercury emissions. “Moreover, ozone season (Could 1 to September 30) NOX emissions decreased by 9% nationwide and 18% for the ten states implementing the Good Neighbor Plan,” it mentioned.
The company prompt the emissions drops resulted primarily from adjustments within the fossil gasoline era combine and improved effectivity. “Knowledge from 2023 present an 18% lower in coal era and an 8% improve in pure fuel era from 2022,” it famous. “From 2022–2023, emission charges at coal amenities for sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides improved by 7% and three%, respectively. Roughly half of this enchancment resulted from models extra successfully working their current controls, and half resulted from elevated utilization of extra extremely managed models.”
—Sonal Patel is a POWER senior affiliate editor (@sonalcpatel, @POWERmagazine)


